Meta-analysis of Montreal cognitive assessment diagnostic accuracy in amnestic mild cognitive impairment
- PMID: 38414877
- PMCID: PMC10896827
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1369766
Meta-analysis of Montreal cognitive assessment diagnostic accuracy in amnestic mild cognitive impairment
Abstract
Background: The Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) is one of the most widely-used cognitive screening instruments and has been translated into several different languages and dialects. Although the original validation study suggested to use a cutoff of ≤26, subsequent studies have shown that lower cutoff values may yield fewer false-positive indications of cognitive impairment. The aim of this study was to summarize the diagnostic accuracy and mean difference of the MoCA when comparing cognitively unimpaired (CU) older adults to those with amnestic mild cognitive impairment (aMCI).
Methods: PubMed and EMBASE databases were searched from inception to 22 February 2022. Meta-analyses for area under the curve (AUC) and standardized mean difference (SMD) values were performed.
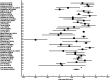
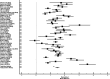
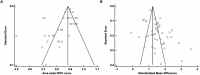
Results: Fifty-five observational studies that included 17,343 CU and 8,413 aMCI subjects were selected for inclusion. Thirty-nine studies were used in the AUC analysis while 44 were used in the SMD analysis. The overall AUC value was 0.84 (95% CI: 0.81, 0.87) indicating good diagnostic accuracy and a large effect size was noted for the SMD analysis (Hedge's g = 1.49, 95% CI: 1.33, 1.64). Both analyses had high levels of between-study heterogeneity. The median cutoff score for identifying aMCI was <24.
Discussion and conclusion: The MoCA has good diagnostic accuracy for detecting aMCI across several different languages. The findings of this meta-analysis also support the use of 24 as the optimal cutoff when the MoCA is used to screen for suspected cognitive impairment.
Keywords: cognitive screen; cognitively unimpaired; cutoff score; diagnostic accuracy; mild cognitive impairment.
Copyright © 2024 Malek-Ahmadi and Nikkhahmanesh.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
-
- Albert M. S., DeKosky S. T., Dickson D., Dubois B., Feldman H. H., Fox N. C., et al. (2011). The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer's disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 7, 270–279. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.008, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bello-Lepe S., Alonso-Sánchez M. F., Ortega A., Gaete M., Veliz M., Lira J., et al. (2020). Montreal cognitive assessment as screening measure for mild and major neurocognitive disorder in a Chilean population. Dement Geriatr Cogn Dis Extra. 10, 105–114. doi: 10.1159/000506280, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

