Practices, Efficacy, and Reported Side Effects Associated with Isotretinoin Treatment in Palestine
- PMID: 38414983
- PMCID: PMC10898599
- DOI: 10.2147/PPA.S442436
Practices, Efficacy, and Reported Side Effects Associated with Isotretinoin Treatment in Palestine
Abstract
Background: Isotretinoin is a commonly prescribed medication for the treatment of acne. It is associated with serious side effects that require monitoring and adherence by patients and healthcare providers. No studies have been conducted in Palestine to explore isotretinoin prescribing and utilization.
Objective: This study aims to evaluate the current clinical practices, adherence to clinical guidelines, efficacy, and reported side effects associated with Isotretinoin treatment in Palestine.
Methods: A descriptive cross-sectional online questionnaire-based study using social media platforms (eg, Facebook and Telegram) was conducted among Birzeit University students in April 2023. This study included participants aged ≥ 18 years with a history of isotretinoin treatment; subjects with incomplete data were excluded. Statistical significance was set at P < 0.05. SPSS version 27 was used for data analysis.
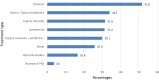
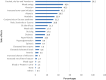
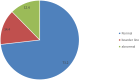
Results: A total of 548 participants were included in the study, the majority of most of whom were female (96%). The most predominant side effects were cracked, dry lips and xeroderma (96.2%). Moreover, 12% of participants had depression. Most respondents were educated about medication side effects and only 39.1% were counseled about blood donation. Of the 59 sexually active women, only 4 (6.8%) were asked for a recent pregnancy test. A total of 60.2% of dermatologists adhered to the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) guidelines, and 48.7% ordered the required laboratory tests before initiating isotretinoin treatment. Only 1.7% of pharmacists followed the FDA-suggested protocols for dispensing isotretinoin to childbearing females.
Conclusion: Adherence to isotretinoin safety prescribing protocols to provide patient education, monitoring, and ordering of laboratories to ensure patient safety can be improved by adapting policies and protocols in pharmacy and medical practice in Palestine to monitor and enforce adherence when prescribing, dispensing, or taking high-risk medications.
Keywords: acne; adherence; guidelines; isotretinoin; side effects.
© 2024 Abukhalil et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescribing Patterns of Isotretinoin for Acne Among Dermatologists in Central Jordan.Cureus. 2024 Apr 23;16(4):e58840. doi: 10.7759/cureus.58840. eCollection 2024 Apr. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38784345 Free PMC article.
-
Patterns of prescribing isotretinoin: focus on women of childbearing potential.Ann Pharmacother. 1992 Feb;26(2):155-61. doi: 10.1177/106002809202600201. Ann Pharmacother. 1992. PMID: 1554922
-
An Assessment of the Knowledge of Oral Isotretinoin (Roaccutane) Treatment Among Pharmacy Students in Saudi Arabia.Cureus. 2023 Jun 13;15(6):e40388. doi: 10.7759/cureus.40388. eCollection 2023 Jun. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37456447 Free PMC article.
-
Oral isotretinoin for acne.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Nov 24;11(11):CD009435. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009435.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30484286 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the effects of isotretinoin on the premature epiphyseal closure in pediatric populations: a literature review.J Osteopath Med. 2021 Oct 11;122(1):45-53. doi: 10.1515/jom-2021-0108. J Osteopath Med. 2021. PMID: 34626532 Review.
Cited by
-
Palestinian dermatology: exploring policies, challenges, and opportunities in fragile and conflict-affected settings.Int J Equity Health. 2025 Jun 12;24(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s12939-025-02551-x. Int J Equity Health. 2025. PMID: 40506742 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chernyshov PV, Tomas-Aragones L, Manolache L, et al. Which acne treatment has the best influence on health-related quality of life? Literature review by the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology Task Force on Quality of Life and Patient Oriented Outcomes. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32(9):1410–1419. doi:10.1111/jdv.15048 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous