Evaluation of HPV 16 and HPV 18 Oncoprotein Expression as Alternative Diagnostic Tools in Cervical Lesion
- PMID: 38415538
- PMCID: PMC11077110
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.2.521
Evaluation of HPV 16 and HPV 18 Oncoprotein Expression as Alternative Diagnostic Tools in Cervical Lesion
Abstract
Objective: The study aimed to evaluate E6 and E7 oncoproteins of HPV16 and HPV18 expression in formalin - fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) tissue in different grades of the cervical lesion and evaluate the potential use of E6 and E7 oncoproteins derived from HPV 16 and 18 as diagnostic protein biomarkers for triaging cervical lesions.
Methodology: A total of 102 FFPE cervical tissues were collected from 2 tertiary hospitals and immunohistochemical reactivity staining of E6 and E7 oncoproteins of HPV16 and HPV18 were evaluated using immunoreactive scoring (IRS) system and analysed statistically.
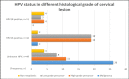
Result: The result showed an increased oncoprotein expression with the progression of cervical lesions. There is a statistically significant association between histology grade and HPV16/18-E6 expression (p = 0.028). However, there are no significant association of histological grade to HPV16-E7 immunoreactivity score (p = 0.264) and HPV18-E7 (p=0.080).
Conclusion: The immunohistochemical expression of HPV oncoproteins is a potential alternative diagnostic tool applicable in a low-resource laboratory setting. The advantage of the histochemical evaluation is that this method is simpler to apply and less expensive in comparison to in situ mRNA hybridization. Nevertheless, our study also found that antibodies against HPV that are commercially available suffer quite substantial specificity issues such as background staining and inconsistency between different batches. Hence, the utilization of antibody-based staining warrants stringent quality control.
Keywords: Cervical lesion; E6; E7; HPV16; HPV18.
Conflict of interest statement
We have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TLR9 expression in uterine cervical lesions of Uyghur women correlate with cervical cancer progression and selective silencing of human papillomavirus 16 E6 and E7 oncoproteins in vitro.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(14):5867-72. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.14.5867. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014. PMID: 25081715
-
In vitro and in vivo growth inhibition of human cervical cancer cells via human papillomavirus E6/E7 mRNAs' cleavage by CRISPR/Cas13a system.Antiviral Res. 2020 Jun;178:104794. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104794. Epub 2020 Apr 14. Antiviral Res. 2020. PMID: 32298665
-
Honeybee venom possesses anticancer and antiviral effects by differential inhibition of HPV E6 and E7 expression on cervical cancer cell line.Oncol Rep. 2015 Apr;33(4):1675-82. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.3760. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25633640
-
Feasibility study of a human papillomavirus E6 and E7 oncoprotein test for the diagnosis of cervical precancer and cancer.J Int Med Res. 2018 Mar;46(3):1033-1042. doi: 10.1177/0300060517736913. Epub 2018 Jan 11. J Int Med Res. 2018. PMID: 29322839 Free PMC article.
-
Usefulness of high-risk HPV early oncoprotein (E6 and E7) serological markers in the detection of cervical cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Med Virol. 2023 Jan;95(1):e27900. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27900. Epub 2022 Jun 9. J Med Virol. 2023. PMID: 35641882 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. WHO Report on Cancer Setting Priorities, Investing Wisely And Providing Care For All 2020 WHO report on cancer: setting priorities, investing wisely and providing care for all [Internet]; 2020. Available from: http://apps.Who.Int/bookorders.
-
- Azizah AM, Hashimah B, Nirmal K, Siti Zubaidah AR, Puteri NA, Nabihah A, et al. Malaysian National Cancer Registry Report 2012-2016. Putrajaya : National Cancer Institute, Ministry of Health, Malaysia; 2019.
-
- Liu J, Yang T, Hu Y, Ye C. The value of hpv e6/e7 mrna quantitative analysis in distinguishing high-grade cervical squamous intraepithelial lesions from low-grade cervical squamous intraepithelial lesions. J Virol Methods. 2021;289:114014. - PubMed
-
- Oyervides-Muñoz MA, Pérez-Maya AA, Rodríguez-Gutiérrez HF, Gómez-Macias GS, Fajardo-Ramírez OR, Treviño V, et al. Understanding the hpv integration and its progression to cervical cancer. Infection, Genetics and Evolution. 2018;61:134–44. - PubMed