Dynamic Changes in Body Composition and Protein Intake in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy: A Preliminary Study
- PMID: 38415542
- PMCID: PMC11077131
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.2.555
Dynamic Changes in Body Composition and Protein Intake in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
Background: Ovarian cancer patients often face poor nutritional status, with body composition (BC) serving as a significant prognostic indicator. Skeletal muscle mass (SMM) and fat-free mass (FFM) are crucial predictors of both survival and hospitalization duration. Increasing protein intake has been linked to improvements in SMM and FFM.
Objective: This study aimed to document the alterations in BC parameters among ovarian cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy and correlate these changes with their nutrient intake.
Methods: Twelve female patients with stage III ovarian cancer who received first-line chemotherapy were categorized based on their body mass indices (BMI). BC parameters were assessed using an 8-point bioelectrical impedance analysis with a frequency of 50 Hz-60 Hz and measurement impedance range of 10 Ω-1000 Ω. Nutrient intake (energy, protein, fat, and carbohydrate) was assessed before (T0), during the 3rd (T3), and 6th cycle of chemotherapy (T6) through 24-hour food recall.
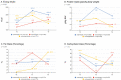
Results: Significant increases in body weight (BW)were observed in the underweight group (from 40.9 to 46.8 kg, p=0.001), concomitant with enhancements in all BC parameters. While changes were noted in SMM, they were not statistically significant (p=0.105).Among the underweight group, a protein intake above 1.2 g/kg BW led to an uptrend trend in SMM. Conversely, FFM in overweight/obese patients decreased significantly (from 37.6 to 36.4 kg, p=0.005) due to a a reduction in body water. Throughout chemotherapy, fat mass (FM), visceral fat (VAT), and phase angle (PhA) increased in all patient groups, reflecting heightened fat and carbohydrate intake.
Conclusion: Among stage III ovarian cancer patients, BC undergoes dynamic changes dynamically during the course of chemotherapy, with more pronounced enhancements observed in FFM among underweight patients. Notably, improvements in PhA, SMM or FFM were particularly evident among underweight patients with a protein intake above 1.2 g/kg BW.
Keywords: Ovarian Cancer; body compositional; nutritional intake.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Body composition and dietary intake in patients with head and neck cancer during radiotherapy: a longitudinal study.BMJ Support Palliat Care. 2023 Dec;13(4):445-452. doi: 10.1136/bmjspcare-2020-002359. Epub 2020 Sep 11. BMJ Support Palliat Care. 2023. PMID: 32917650
-
Phase angle is associated with cardiorespiratory fitness and body composition in children aged between 9 and 11 years.Physiol Behav. 2020 Mar 1;215:112772. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2019.112772. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Physiol Behav. 2020. PMID: 31837386
-
Dynamic Nutrition Strategies for Anorexia Nervosa: Marker-Based Integration of Calories and Proteins.Nutrients. 2025 Jan 31;17(3):560. doi: 10.3390/nu17030560. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 39940418 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Body Weight and Body Composition on Ovarian Cancer Prognosis.Curr Oncol Rep. 2016 Feb;18(2):8. doi: 10.1007/s11912-015-0488-3. Curr Oncol Rep. 2016. PMID: 26769113 Review.
-
Measurement of lean body mass using bioelectrical impedance analysis: a consideration of the pros and cons.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2017 Aug;29(4):591-597. doi: 10.1007/s40520-016-0622-6. Epub 2016 Aug 27. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2017. PMID: 27568020 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of diet, obesity and body composition in epithelial ovarian cancer development and progression: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications.Gynecol Oncol Rep. 2025 Mar 16;58:101718. doi: 10.1016/j.gore.2025.101718. eCollection 2025 Apr. Gynecol Oncol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40213527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness of High-Protein Energy-Dense Oral Supplements on Patients with Malnutrition Using Morphofunctional Assessment with AI-Assisted Muscle Ultrasonography: A Real-World One-Arm Study.Nutrients. 2024 Sep 17;16(18):3136. doi: 10.3390/nu16183136. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39339736 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49. - PubMed
-
- Prabowo A TB, Utomo B. Correlation between clinicopathological factors and clinical outcomes of recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer at a tertiary hospital in surabaya. Bali Med J. 2022;11(2):807–12.
-
- Webb PM, Jordan SJ. Epidemiology of epithelial ovarian cancer. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2017;41:3–14. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

