High Expression of PXMP4 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Tissues
- PMID: 38415547
- PMCID: PMC11077113
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.2.603
High Expression of PXMP4 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Tissues
Abstract
Objective: To analyze the high expression of peroxisome membrane protein 4 (PXMP4) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and its clinical significance.
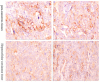
Methods: The expression of PXMP4 mRNA in HCC tissues and corresponding adjacent tissues was detected by Q-PCR, and the expression of PXMP4 protein was detected by Western blot and immunohistochemistry. The correlation of PXMP4 protein expression with clinicopathological features and prognosis of HCC was analyzed.
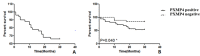
Results: The expression levels of PXMP4 mRNA and protein in HCC tissues were significantly higher than those in adjacent tissues (P < 0.05), and its high expression was significantly correlated with tumor differentiation, lymph node metastasis, depth of invasion and TNM stage (P < 0.05). Patients with high expression of PXMP4 had a poor prognosis (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: The high expression of PXMP4 may promote the occurrence and development of HCC, and inhibition of PXMP4 may be one of the potential molecular targets for targeted therapy of HCC.
Keywords: Keywords: Hepatocellular Carcinoma; PXMP4; Prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Down-regulation of the tumour suppressor κ-opioid receptor predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma patients.BMC Cancer. 2017 Aug 18;17(1):553. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3541-9. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28821282 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression of IQGAP1/2 in Hepatocellular carcinoma and its relationship with clinical outcomes.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(12):4951-6. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.12.4951. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014. PMID: 24998570
-
Clinical significance of high expression of stanniocalcin-2 in hepatocellular carcinoma.Biosci Rep. 2019 Apr 26;39(4):BSR20182057. doi: 10.1042/BSR20182057. Print 2019 Apr 30. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30962272 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinical significance of RYBP expression in primary hepatocellular carcinoma].Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2019 Apr 28;44(4):399-405. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2019.04.009. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2019. PMID: 31113915 Chinese.
-
Prognostic value of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 in hepatocellular carcinoma: A study based on multi-omics analysis and RT-PCR validation.Pathol Oncol Res. 2023 Jan 4;28:1610808. doi: 10.3389/pore.2022.1610808. eCollection 2022. Pathol Oncol Res. 2023. PMID: 36685103 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. - PubMed
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Montal R, Sia D, Finn RS. Molecular therapies and precision medicine for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2018;15(10):599–616. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases