Viabahn stent graft for arterial injury management: safety, technical success, and long-term outcome
- PMID: 38416319
- PMCID: PMC10900043
- DOI: 10.1186/s42155-024-00435-9
Viabahn stent graft for arterial injury management: safety, technical success, and long-term outcome
Abstract
Background: The Viabahn stent graft has emerged as an integral tool for managing vascular diseases, but there is limited long-term data on its performance in emergency endovascular treatment. This study aimed to assess safety, technical success, and long-term efficacy of the Viabahn stent graft in emergency treatment of arterial injury.
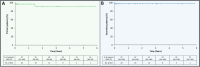
Methods: We conducted a retrospective single tertiary centre analysis of patients who underwent Viabahn emergency arterial injury treatment between 2015 and 2020. Indication, intraoperative complications, technical and clinical success, and major adverse events at 30 days were evaluated. Secondary efficacy endpoints were the primary and secondary patency rates assessed by Kaplan-Meier analysis.
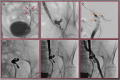
Results: Forty patients (71 ± 13 years, 19 women) were analyzed. Indications for Viabahn emergency treatment were extravasation (65.0%), arterio-venous fistula (22.5%), pseudoaneurysm (10.0%), and arterio-ureteral fistula (2.5%). No intraoperative adverse events occurred, technical and clinical success rates were 100%. One acute stent graft occlusion occurred in the popliteal artery on day 9, resulting in a 30-day device-related major-adverse-event rate of 2.5%. Median follow-up was 402 days [IQR, 43-1093]. Primary patency rate was 97% (95% CI: 94-100) in year 1, and 92% (95% CI: 86-98) from years 2 to 6. One stent graft occlusion occurred in the external iliac artery at 18 months; successful revascularization resulted in secondary patency rates of 97% (95% CI: 94-100) from years 1 to 6.
Conclusion: Using Viabahn stent graft in emergency arterial injury treatment had 100% technical and clinical success rates, a low 30-day major-adverse-event rate of 2.5%, and excellent long-term patency rates.
Keywords: Bleeding; Endoprosthesis; Graft; Heparin; Injury; Stent; Viabahn.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Lammer J, Zeller T, Hausegger KA, Schaefer PJ, Gschwendtner M, Mueller-Huelsbeck S, et al. Heparin-bonded covered stents versus bare-metal stents for complex femoropopliteal artery lesions: the randomized VIASTAR trial (Viabahn endoprosthesis with PROPATEN bioactive surface [VIA] versus bare nitinol stent in the treatment of long lesions in superficial femoral artery occlusive disease). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62(15):1320–7. 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.05.079. - PubMed
-
- Geraghty PJ, Mewissen MW, Jaff MR, Ansel GM. Three-year results of the VIBRANT trial of VIABAHN endoprosthesis versus bare nitinol stent implantation for complex superficial femoral artery occlusive disease. J Vasc Surg. 2013;58(2):386–395e4. 10.1016/j.jvs.2013.01.050. - PubMed
-
- Aboyans V, Ricco JB, Bartelink MLEL, Björck M, Brodmann M, Cohnert T, et al. 2017 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of peripheral arterial diseases, in collaboration with the European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) Eur Heart J. 2018;39(9):763–816. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx095. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fox N, Rajani RR, Bokhari F, Chiu WC, Kerwin A, Seamon MJ, et al. Evaluation and management of penetrating lower extremity arterial trauma: an eastern association for the surgery of trauma practice management guideline. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012;73(5 SUPPL4):315–20. 10.1097/TA.0b013e31827018e4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
