Role of SIRT1 in Potentially Toxic Trace Elements (Lead, Fluoride, Aluminum and Cadmium) Associated Neurodevelopmental Toxicity
- PMID: 38416341
- PMCID: PMC11502598
- DOI: 10.1007/s12011-024-04116-5
Role of SIRT1 in Potentially Toxic Trace Elements (Lead, Fluoride, Aluminum and Cadmium) Associated Neurodevelopmental Toxicity
Abstract
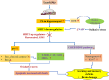
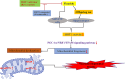
The formation of the central nervous system is a meticulously planned and intricate process. Any modification to this process has the potential to disrupt the structure and operation of the brain, which could result in deficiencies in neurological growth. When neurotoxic substances are present during the early stages of development, they can be exceptionally dangerous. Prenatally, the immature brain is extremely vulnerable and is therefore at high risk in pregnant women associated with occupational exposures. Lead, fluoride, aluminum, and cadmium are examples of possibly toxic trace elements that have been identified as an environmental concern in the aetiology of a number of neurological and neurodegenerative illnesses. SIRT1, a member of the sirtuin family has received most attention for its potential neuroprotective properties. SIRT1 is an intriguing therapeutic target since it demonstrates important functions to increase neurogenesis and cellular lifespan by modulating multiple pathways. It promotes axonal extension, neurite growth, and dendritic branching during the development of neurons. Additionally, it contributes to neurogenesis, synaptic plasticity, memory development, and neuroprotection. This review summarizes the possible role of SIRT1 signalling pathway in potentially toxic trace elements -induced neurodevelopmental toxicity, highlighting some molecular pathways such as mitochondrial biogenesis, CREB/BDNF and PGC-1α/NRF1/TFAM.
Keywords: Memory; Mitochondrial dysfunction; Neurogenesis; Neurotoxicity; SIRT1.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SIRT1-dependent mitochondrial biogenesis supports therapeutic effects of resveratrol against neurodevelopment damage by fluoride.Theranostics. 2020 Mar 26;10(11):4822-4838. doi: 10.7150/thno.42387. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32308752 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial biogenesis: pharmacological approaches.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(35):5507-9. doi: 10.2174/138161282035140911142118. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 24606795
-
SIRT1 Regulates Mitochondrial Damage in N2a Cells Treated with the Prion Protein Fragment 106-126 via PGC-1α-TFAM-Mediated Mitochondrial Biogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 7;25(17):9707. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179707. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273653 Free PMC article.
-
Role of mitochondria in diabetic peripheral neuropathy: Influencing the NAD+-dependent SIRT1-PGC-1α-TFAM pathway.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2019;145:177-209. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2019.04.002. Epub 2019 Jun 8. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 31208524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SIRT1 in neurodevelopment and brain senescence.Neuron. 2014 Feb 5;81(3):471-83. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.01.028. Neuron. 2014. PMID: 24507186 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chondroitin sulfate protects against synaptic impairment caused by fluorosis through the Erk1/2-MMP-9 signaling pathway.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 13;15(1):29760. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14631-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40804089 Free PMC article.
-
Metal Toxicity and Dementia Including Frontotemporal Dementia: Current State of Knowledge.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Aug 1;13(8):938. doi: 10.3390/antiox13080938. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199184 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of SIRT1-BDNF Signaling Pathway in Fluoride-Induced Toxicity for Glial BV-2 Cells.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025 Sep;203(9):4789-4806. doi: 10.1007/s12011-024-04503-y. Epub 2025 Jan 17. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025. PMID: 39825065 Free PMC article.
-
Pregnancy and Postpartum Effects of Electronic Cigarettes on Maternal Health and Vascular Function in the Fourth Trimester.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2025 Mar;25(3):325-340. doi: 10.1007/s12012-025-09961-x. Epub 2025 Jan 22. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39841346 Free PMC article.
-
Eucalyptol Attenuates Lead-Induced Anxiety-like Behaviors by Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation, Modulating SIRT1/NF-κB Signaling, and Upregulating BDNF Expression.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025 Apr 9. doi: 10.1007/s12011-025-04616-y. Online ahead of print. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025. PMID: 40205256
References
-
- Grandjean P, Landrigan PJ (2006) Developmental neurotoxicity of industrial chemicals. Lancet 368(9553):2167–2178. 10.1016/s0140-6736(06)69665-7 - PubMed
-
- Miodovnik A (2011) Environmental neurotoxicants and developing brain. Mt Sinai J Medicine: J Translational Personalized Med 78(1):58–77. 10.1002/MSJ - PubMed
-
- Shaik PS, Pachava S (2017) The role of vitamins and trace elements on oral health: a systematic review. Int J Med Reviews 4(1):22–31. 10.29252/ijmr-040105
-
- Afridi HI, Kazi TG, Kazi NG, Jamali MK, Arain MB, Sirajuddin, … Baig JA (2009) Evaluation of arsenic, cobalt, copper and manganese in biological samples of steel mill workers by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Toxicol Ind Health 25(1):59–69. 10.1177/0748233709103036 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

