Recent Progress in Photoreceptor Cell-Based Therapy for Degenerative Retinal Disease
- PMID: 38417110
- PMCID: PMC11016853
- DOI: 10.1093/stcltm/szae005
Recent Progress in Photoreceptor Cell-Based Therapy for Degenerative Retinal Disease
Abstract
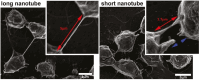
Age-related macular degeneration and retinitis pigmentosa are degenerative retinal diseases that cause severe vision loss. Early clinical trials involving transplantation of photoreceptors as treatment for these conditions are underway. In this review, we summarize recent progress in the field of photoreceptor transplantation, including some pertinent results regarding photoreceptor manufacture, photoreceptor transplantation, mechanisms of donor-host cell integration such as material transfer and photoreceptor transplant immunology. We conclude by proposing several approaches that may provide a rational basis for selecting a vision restoration strategy (eg, donor-host synapse formation vs donor-host nanotube formation) and improved transplant efficiency.
Keywords: cell transplantation; embryonic stem cells; geographic atrophy; induced pluripotent stem cells; macular degeneration; retina; retinal pigment epithelium; retinitis pigmentosa.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
Marco A. Zarbin: Consultant for Boehringer Ingelheim, EdiGene, Genentech/Roche, Illuminare, Life Biosciences, Novartis Pharma AG, Perfuse Therapeutics, Seeing Medicines, Tamarix Pharmaceuticals, Tenpoint Therapeutics; Equity: NVasc. The other authors declared no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Recent Progress in Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cell-Based Therapy for Retinal Disease.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2024 Apr 15;13(4):317-331. doi: 10.1093/stcltm/szae004. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38394392 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stem Cell-based Treatment Strategies for Degenerative Diseases of the Retina.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;17(3):214-225. doi: 10.2174/1574888X16666210804112104. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 34348629 Free PMC article.
-
Photoreceptor cell replacement in macular degeneration and retinitis pigmentosa: A pluripotent stem cell-based approach.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2019 Jul;71:1-25. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2019.03.001. Epub 2019 Mar 16. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2019. PMID: 30885665 Review.
-
Transplantation of photoreceptors into the degenerative retina: Current state and future perspectives.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2019 Mar;69:1-37. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2018.11.001. Epub 2018 Nov 13. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2019. PMID: 30445193 Review.
-
Organoid technology for retinal repair.Dev Biol. 2018 Jan 15;433(2):132-143. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.09.028. Epub 2017 Dec 25. Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29291970 Review.
Cited by
-
In Vivo Cone Photoreceptor Topography of the Human Foveola.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025 Aug 1;66(11):13. doi: 10.1167/iovs.66.11.13. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025. PMID: 40767443 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular analysis of RAX2-regulated retinal development using human retinal organoids at a single-cell resolution.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jun 5;13:1609826. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1609826. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40538981 Free PMC article.
-
Human iPSC-derived neural stem cells displaying radial glia signature exhibit long-term safety in mice.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 1;15(1):9433. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53613-7. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39487141 Free PMC article.
-
Human cone photoreceptor transplantation stimulates remodeling and restores function in AIPL1 model of end-stage Leber congenital amaurosis.Stem Cell Reports. 2025 Apr 8;20(4):102470. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2025.102470. Epub 2025 Mar 27. Stem Cell Reports. 2025. PMID: 40154478 Free PMC article.
-
A Personal Scientific Journey in Ophthalmology: Twenty-Five Years of Translating Research into Novel Therapies.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jun 12;18(6):883. doi: 10.3390/ph18060883. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40573278 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

