Cryptographic approaches to authenticating synthetic DNA sequences
- PMID: 38418329
- PMCID: PMC11309913
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2024.02.002
Cryptographic approaches to authenticating synthetic DNA sequences
Abstract
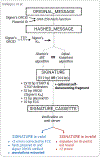
In a bioeconomy that relies on synthetic DNA sequences, the ability to ensure their authenticity is critical. DNA watermarks can encode identifying data in short sequences and can be combined with error correction and encryption protocols to ensure that sequences are robust to errors and securely communicated. New digital signature techniques allow for public verification that a sequence has not been modified and can contain sufficient information for synthetic DNA to be self-documenting. In translating these techniques from bacteria to more complex genetically modified organisms (GMOs), special considerations must be made to allow for public verification of these products. We argue that these approaches should be widely implemented to assert authorship, increase the traceability, and detect the unauthorized use of synthetic DNA.
Keywords: DNA cryptography; DNA watermark; cyberbiosecurity; digital signature; genetic engineering attribution.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests J.P. and S.P. have financial interests in GenoFAB, Inc. This company may benefit or be perceived as benefiting from this publication.
Figures



References
-
- Peccoud J et al. (2018) Cyberbiosecurity: from naive trust to risk awareness. Trends in biotechnology 36, 4–7 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

