NRF2 in kidney physiology and disease
- PMID: 38418382
- PMCID: PMC10901725
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.15961
NRF2 in kidney physiology and disease
Abstract
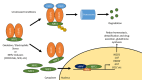
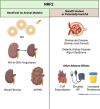
The role of NRF2 in kidney biology has received considerable interest over the past decade. NRF2 transcriptionally controls genes responsible for cellular protection against oxidative and electrophilic stress and has anti-inflammatory functions. NRF2 is expressed throughout the kidney and plays a role in salt and water handling. In disease, animal studies show that NRF2 protects against tubulointerstitial damage and reduces interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy, and may slow progression of polycystic kidney disease. However, the role of NRF2 in proteinuric glomerular diseases is controversial. Although the NRF2 inducer, bardoxolone methyl (CDDO-Me), increases glomerular filtration rate in humans, it has not been shown to slow disease progression in diabetic kidney disease and Alport syndrome. Furthermore, bardoxolone methyl was associated with negative effects on fluid retention, proteinuria, and blood pressure. Several animal studies replicate findings of worsened proteinuria and a more rapid progression of kidney disease, although considerable controversy exists. It is clear that further study is needed to better understand the effects of NRF2 in the kidney. This review summarizes the available data to clarify the promise and risks associated with targeting NRF2 activity in the kidney.
Keywords: bardoxolone methyl; chronic kidney disease; electrophiles; oxidative stress; proteinuria.
© 2024 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society. This article has been contributed to by U.S. Government employees and their work is in the public domain in the USA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bardoxolone methyl analog attenuates proteinuria-induced tubular damage by modulating mitochondrial function.FASEB J. 2019 Nov;33(11):12253-12263. doi: 10.1096/fj.201900217R. Epub 2019 Aug 30. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 31431054 Free PMC article.
-
Bardoxolone ameliorates TGF-β1-associated renal fibrosis through Nrf2/Smad7 elevation.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 Jul;138:33-42. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.04.033. Epub 2019 May 3. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 31059771
-
Bardoxolone methyl: drug development for diabetic kidney disease.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2020 Oct;24(10):857-864. doi: 10.1007/s10157-020-01917-5. Epub 2020 Jun 27. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32594372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dose-dependent deleterious and salutary actions of the Nrf2 inducer dh404 in chronic kidney disease.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Sep;86:374-81. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.04.022. Epub 2015 Apr 28. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 25930007
-
[Challenges in kidney disease: therapeutic potential of bardoxolone methyl].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2022;157(4):261-264. doi: 10.1254/fpj.22007. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2022. PMID: 35781457 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Endothelial NOX5 Obliterates the Reno-Protective Effect of Nox4 Deletion by Promoting Renal Fibrosis via Activation of EMT and ROS-Sensitive Pathways in Diabetes.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Mar 26;13(4):396. doi: 10.3390/antiox13040396. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38671844 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccarin suppresses diabetic nephropathy through inhibiting the EGFR/ERK1/2 signaling pathway.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024 Aug 27;56(12):1860-1874. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2024141. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024. PMID: 39205643 Free PMC article.
-
NRF2 Dysregulation and Therapeutic Insights Across Chronic Kidney Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 2;26(15):7471. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157471. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of Nrf2 activation in a proteinuric Alport syndrome mouse model.Life Sci Alliance. 2025 Jun 17;8(8):e202503330. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202503330. Print 2025 Aug. Life Sci Alliance. 2025. PMID: 40527586 Free PMC article.
-
Bardoxolone displays potent activity against triple negative breast cancer by inhibiting the TRIP13/STAT3 circuit.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025 Jun;46(6):1733-1741. doi: 10.1038/s41401-025-01481-2. Epub 2025 Feb 12. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025. PMID: 39939802
References
-
- Aminzadeh, M. A. , Reisman, S. A. , Vaziri, N. D. , Khazaeli, M. , Yuan, J. , & Meyer, C. J. (2014). The synthetic triterpenoid RTA dh404 (CDDO‐dhTFEA) restores Nrf2 activity and attenuates oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis in rats with chronic kidney disease. Xenobiotica, 44, 570–578. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Basile, D. P. , Bonventre, J. V. , Mehta, R. , Nangaku, M. , Unwin, R. , Rosner, M. H. , Kellum, J. A. , Ronco, C. , & Group AXW . (2016). Progression after AKI: Understanding maladaptive repair processes to predict and identify therapeutic treatments. Journal of American Society of Nephrology, 27, 687–697. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

