Functional regulation of aquaporin dynamics by lipid bilayer composition
- PMID: 38418487
- PMCID: PMC10901782
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-46027-y
Functional regulation of aquaporin dynamics by lipid bilayer composition
Abstract
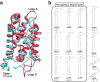
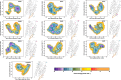
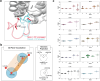
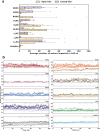
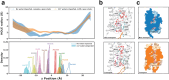
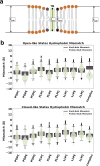
With the diversity of lipid-protein interactions, any observed membrane protein dynamics or functions directly depend on the lipid bilayer selection. However, the implications of lipid bilayer choice are seldom considered unless characteristic lipid-protein interactions have been previously reported. Using molecular dynamics simulation, we characterize the effects of membrane embedding on plant aquaporin SoPIP2;1, which has no reported high-affinity lipid interactions. The regulatory impacts of a realistic lipid bilayer, and nine different homogeneous bilayers, on varying SoPIP2;1 dynamics are examined. We demonstrate that SoPIP2;1's structure, thermodynamics, kinetics, and water transport are altered as a function of each membrane construct's ensemble properties. Notably, the realistic bilayer provides stabilization of non-functional SoPIP2;1 metastable states. Hydrophobic mismatch and lipid order parameter calculations further explain how lipid ensemble properties manipulate SoPIP2;1 behavior. Our results illustrate the importance of careful bilayer selection when studying membrane proteins. To this end, we advise cautionary measures when performing membrane protein molecular dynamics simulations.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Update of
-
Functional Regulation of Aquaporin Dynamics by Lipid Bilayer Composition.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jul 22:2023.07.20.549977. doi: 10.1101/2023.07.20.549977. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Commun. 2024 Feb 28;15(1):1848. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46027-y. PMID: 37502896 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

