BTLA contributes to acute-on-chronic liver failure infection and mortality through CD4+ T-cell exhaustion
- PMID: 38418488
- PMCID: PMC10901893
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-46047-8
BTLA contributes to acute-on-chronic liver failure infection and mortality through CD4+ T-cell exhaustion
Abstract
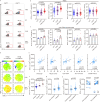
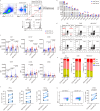
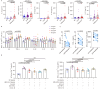
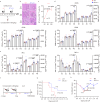
B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) levels are increased in patients with hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure (HBV-ACLF). This condition is characterized by susceptibility to infection and T-cell immune exhaustion. However, whether BTLA can induce T-cell immune exhaustion and increase the risk of infection remains unclear. Here, we report that BTLA levels are significantly increased in the circulating and intrahepatic CD4+ T cells from patients with HBV-ACLF, and are positively correlated with disease severity, prognosis, and infection complications. BTLA levels were upregulated by the IL-6 and TNF signaling pathways. Antibody crosslinking of BTLA activated the PI3K-Akt pathway to inhibit the activation, proliferation, and cytokine production of CD4+ T cells while promoting their apoptosis. In contrast, BTLA knockdown promoted their activation and proliferation. BTLA-/- ACLF mice exhibited increased cytokine secretion, and reduced mortality and bacterial burden. The administration of a neutralizing anti-BTLA antibody reduced Klebsiella pneumoniae load and mortality in mice with ACLF. These data may help elucidate HBV-ACLF pathogenesis and aid in identifying novel drug targets.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82370604/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82003864/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81670528/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81670528/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 2023J01239, 2019J01593/Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (Fujian Provincial Natural Science Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

