Machine learning driven web-based app platform for the discovery of monoamine oxidase B inhibitors
- PMID: 38418571
- PMCID: PMC10901862
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-55628-y
Machine learning driven web-based app platform for the discovery of monoamine oxidase B inhibitors
Abstract
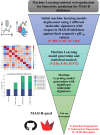
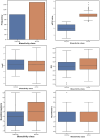
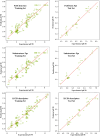
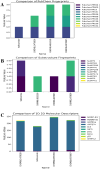
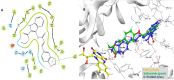
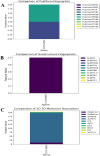
Monoamine oxidases (MAOs), specifically MAO-A and MAO-B, play important roles in the breakdown of monoamine neurotransmitters. Therefore, MAO inhibitors are crucial for treating various neurodegenerative disorders, including Parkinson's disease (PD), Alzheimer's disease (AD), and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). In this study, we developed a novel cheminformatics pipeline by generating three diverse molecular feature-based machine learning-assisted quantitative structural activity relationship (ML-QSAR) models concerning MAO-B inhibition. PubChem fingerprints, substructure fingerprints, and one-dimensional (1D) and two-dimensional (2D) molecular descriptors were implemented to unravel the structural insights responsible for decoding the origin of MAO-B inhibition in 249 non-reductant molecules. Based on a random forest ML algorithm, the final PubChem fingerprint, substructure fingerprint, and 1D and 2D molecular descriptor prediction models demonstrated significant robustness, with correlation coefficients of 0.9863, 0.9796, and 0.9852, respectively. The significant features of each predictive model responsible for MAO-B inhibition were extracted using a comprehensive variance importance plot (VIP) and correlation matrix analysis. The final predictive models were further developed as a web application, MAO-B-pred ( https://mao-b-pred.streamlit.app/ ), to allow users to predict the bioactivity of molecules against MAO-B. Molecular docking and dynamics studies were conducted to gain insight into the atomic-level molecular interactions between the ligand-receptor complexes. These findings were compared with the structural features obtained from the ML-QSAR models, which supported the mechanistic understanding of the binding phenomena. The presented models have the potential to serve as tools for identifying crucial molecular characteristics for the rational design of MAO-B target inhibitors, which may be used to develop effective drugs for neurodegenerative disorders.
Keywords: 1D and 2D molecular descriptors; Bioactivity; ML-QSAR; Molecular docking; Molecular dynamics simulation; Molecular interactions; Monoamine oxidase B; Prediction models; PubChem fingerprints; Substructure fingerprints; Web application.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Proposing Novel MAO-B Hit Inhibitors Using Multidimensional Molecular Modeling Approaches and Application of Binary QSAR Models for Prediction of Their Therapeutic Activity, Pharmacokinetic and Toxicity Properties.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2018 Jul 18;9(7):1768-1782. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00095. Epub 2018 May 7. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29671581
-
Understanding the Molecular Determinant of Reversible Human Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors Containing 2H-Chromen-2-One Core: Structure-Based and Ligand-Based Derived Three-Dimensional Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationships Predictive Models.J Chem Inf Model. 2017 Apr 24;57(4):787-814. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.6b00608. Epub 2017 Mar 30. J Chem Inf Model. 2017. PMID: 28291352
-
Developing a Multi-target Model to Predict the Activity of Monoamine Oxidase A and B Drugs.Curr Top Med Chem. 2020;20(18):1593-1600. doi: 10.2174/1568026620666200603121224. Curr Top Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32493193
-
Predicting monoamine oxidase inhibitory activity through ligand-based models.Curr Top Med Chem. 2012;12(20):2258-74. doi: 10.2174/156802612805219987. Curr Top Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 23231398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic, Molecular and Computational Aspects of Novel Monoamine Oxidase (MAO) Inhibitors.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2017;20(6):492-509. doi: 10.2174/1386207320666170310121337. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2017. PMID: 28294055 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring putative drug properties associated with TNF-alpha inhibition and identification of potential targets in cardiovascular disease using machine learning-assisted QSAR modeling and virtual reverse pharmacology approach.Mol Divers. 2024 Aug;28(4):2263-2287. doi: 10.1007/s11030-024-10921-w. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Mol Divers. 2024. PMID: 38954070
-
Dual inhibition of AChE and MAO-B in Alzheimer's disease: machine learning approaches and model interpretations.Mol Divers. 2025 Aug;29(4):3113-3130. doi: 10.1007/s11030-024-11061-x. Epub 2025 Jan 21. Mol Divers. 2025. PMID: 39838228
-
Machine Learning-Based High-Throughput Screening, Molecular Modeling and Quantum Chemical Analysis to Investigate Mycobacterium tuberculosis MetRS Inhibitors.ChemistryOpen. 2025 Jul;14(7):e202400460. doi: 10.1002/open.202400460. Epub 2025 Feb 25. ChemistryOpen. 2025. PMID: 39996268 Free PMC article.
-
EGFRAP: a predictive machine learning model for assessing small molecule activity against the epidermal growth factor receptor.RSC Med Chem. 2025 Jul 10. doi: 10.1039/d5md00361j. Online ahead of print. RSC Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40718840 Free PMC article.
-
New class of thio/semicarbazide-based benzyloxy derivatives as selective class of monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 28;14(1):31292. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82771-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39732801 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdelgawad MA, et al. Development of bromo-and fluoro-based α, β-unsaturated ketones as highly potent MAO-B inhibitors for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. J. Mol. Struct. 2022;1266:133545. doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.133545. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

