Cellular reprogramming as a tool to model human aging in a dish
- PMID: 38418829
- PMCID: PMC10902382
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-46004-5
Cellular reprogramming as a tool to model human aging in a dish
Abstract
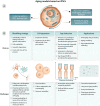
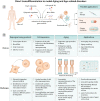
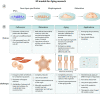
The design of human model systems is highly relevant to unveil the underlying mechanisms of aging and to provide insights on potential interventions to extend human health and life span. In this perspective, we explore the potential of 2D or 3D culture models comprising human induced pluripotent stem cells and transdifferentiated cells obtained from aged or age-related disorder-affected donors to enhance our understanding of human aging and to catalyze the discovery of anti-aging interventions.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-Aging Strategies Based on Cellular Reprogramming.Trends Mol Med. 2016 Aug;22(8):725-738. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2016.06.005. Epub 2016 Jul 14. Trends Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27426043 Review.
-
Mechanisms of cellular rejuvenation.FEBS Lett. 2019 Dec;593(23):3381-3392. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13483. Epub 2019 Jun 24. FEBS Lett. 2019. PMID: 31197818 Review.
-
Rapamycin and other longevity-promoting compounds enhance the generation of mouse induced pluripotent stem cells.Aging Cell. 2011 Oct;10(5):908-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2011.00722.x. Epub 2011 Jun 14. Aging Cell. 2011. PMID: 21615676
-
Aging in a Dish: iPSC-Derived and Directly Induced Neurons for Studying Brain Aging and Age-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases.Annu Rev Genet. 2018 Nov 23;52:271-293. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-120417-031534. Epub 2018 Sep 12. Annu Rev Genet. 2018. PMID: 30208291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular reprogramming: A new way to understand aging mechanisms.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2018 Mar;7(2). doi: 10.1002/wdev.308. Epub 2018 Jan 19. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29350802 Review.
Cited by
-
3D Models Currently Proposed to Investigate Human Skin Aging and Explore Preventive and Reparative Approaches: A Descriptive Review.Biomolecules. 2024 Aug 26;14(9):1066. doi: 10.3390/biom14091066. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39334833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Skin health and biological aging.Nat Aging. 2025 Jul;5(7):1195-1206. doi: 10.1038/s43587-025-00901-6. Epub 2025 Jun 17. Nat Aging. 2025. PMID: 40527938 Review.
-
A longevity-specific bank of induced pluripotent stem cells from centenarians and their offspring.Aging Cell. 2025 Jan;24(1):e14351. doi: 10.1111/acel.14351. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Aging Cell. 2025. PMID: 39319670 Free PMC article.
-
The Hidden Dangers of Sedentary Living: Insights into Molecular, Cellular, and Systemic Mechanisms.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 6;25(19):10757. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910757. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39409085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Skin and Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells as Biomarkers for Neurodegenerative Diseases.Genes (Basel). 2024 Nov 25;15(12):1507. doi: 10.3390/genes15121507. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39766775 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

