Set-up of a pharmaceutical cell bank of Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense MSR1 magnetotactic bacteria producing highly pure magnetosomes
- PMID: 38419080
- PMCID: PMC10903015
- DOI: 10.1186/s12934-024-02313-4
Set-up of a pharmaceutical cell bank of Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense MSR1 magnetotactic bacteria producing highly pure magnetosomes
Abstract
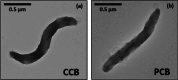
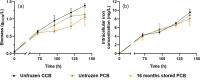
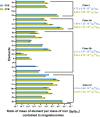
We report the successful fabrication of a pharmaceutical cellular bank (PCB) containing magnetotactic bacteria (MTB), which belong to the Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense MSR1 species. To produce such PCB, we amplified MTB in a minimal growth medium essentially devoid of other heavy metals than iron and of CMR (Carcinogenic, mutagenic and reprotoxic) products. The PCB enabled to acclimate MTB to such minimal growth conditions and then to produce highly pure magnetosomes composed of more than 99.9% of iron. The qualification of the bank as a PCB relies first on a preserved identity of the MTB compared with the original strain, second on genetic bacterial stability observed over 100 generations or under cryo-preservation for 16 months, third on a high level of purity highlighted by an absence of contaminating microorganisms in the PCB. Furthermore, the PCB was prepared under high-cell load conditions (9.108 cells/mL), allowing large-scale bacterial amplification and magnetosome production. In the future, the PCB could therefore be considered for commercial as well as research orientated applications in nanomedicine. We describe for the first-time conditions for setting-up an effective pharmaceutical cellular bank preserving over time the ability of certain specific cells, i.e. Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense MSR1 MTB, to produce nano-minerals, i.e. magnetosomes, within a pharmaceutical setting.
Keywords: Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense MSR1; Cell Bank; Fed-batch cultivation; Magnetosome; Magnetotactic bacterium; Minimal medium; Pharmaceutical grade nanoparticle; Scale-up.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
TC, RL, IC and EA declare that they have been working in the start-up Nanobacterie. KB and FG declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abreu FP, Silva KT, Farina M, Keim CN, Lins U. Greigite magnetosome membrane ultrastructure in “Candidatus Magnetoglobus multicellularis”. Int Microbiol. 2008;11:75–80. - PubMed
-
- Alphandéry E, Lijeour L, Lalatonne Y, Motte L. Different signatures between chemically and biologically synthesized nanoparticles in a magnetic sensor: a new technology for multiparametric detection. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2010;147:786–790. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2010.04.009. - DOI
-
- Alphandéry E, Abi Haidar D, Seksek O, Guyot F, Chebbi I. Fluorescent magnetosomes for controlled and repetitive drug release under the application of an alternating magnetic field under conditions of limited temperature increase (<2.5 °C) Nanoscale. 2018;10:10918–10933. doi: 10.1039/C8NR02164C. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

