A review on traditional Chinese medicine natural products and acupuncture intervention for Alzheimer's disease based on the neuroinflammatory
- PMID: 38419106
- PMCID: PMC10900670
- DOI: 10.1186/s13020-024-00900-6
A review on traditional Chinese medicine natural products and acupuncture intervention for Alzheimer's disease based on the neuroinflammatory
Abstract
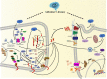
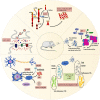
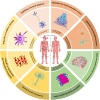
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease with insidious onset and progressive development. It is clinically characterized by cognitive impairment, memory impairment and behavioral change. Chinese herbal medicine and acupuncture are important components of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), and are commonly used in clinical treatment of AD. This paper systematically summarizes the research progress of traditional Chinese medicine natural products and acupuncture treatment of AD, which combined with existing clinical and preclinical evidence, based on a comprehensive review of neuroinflammation, and discusses the efficacy and potential mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine natural products and acupuncture treatment of AD. Resveratrol, curcumin, kaempferol and other Chinese herbal medicine components can significantly inhibit the neuroinflammation of AD in vivo and in vitro, and are candidates for the treatment of AD. Acupuncture can alleviate the memory and cognitive impairment of AD by improving neuroinflammation, synaptic plasticity, nerve cell apoptosis and reducing the production and aggregation of amyloid β protein (Aβ) in the brain. It has the characteristics of early, safe, effective and benign bidirectional adjustment. The purpose of this paper is to provide a basis for improving the clinical strategies of TCM for the treatment of AD.
Keywords: Acupuncture; Alzheimer’s disease; Efficacy and mechanism; Neuroinflammation; Traditional Chinese medicine natural products.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Traditional Chinese Medicine: Role in Reducing β-Amyloid, Apoptosis, Autophagy, Neuroinflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Mitochondrial Dysfunction of Alzheimer's Disease.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Apr 22;11:497. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00497. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32390843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of Alzheimer's disease by combination of acupuncture and Chinese medicine based on pathophysiological mechanism: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Dec 9;101(49):e32218. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032218. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36626477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress in the mechanism of acupuncture regulating microglia in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.Front Neurosci. 2024 Jul 31;18:1435082. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1435082. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39145293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress of Chinese Medicine in Regulating Microglial Polarization against Alzheimer's Disease.Am J Chin Med. 2024;52(8):2255-2275. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X24500873. Epub 2024 Dec 24. Am J Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 39721955 Review.
-
Traditional Chinese Medicine-derived formulations and extracts modulating the PI3K/AKT pathway in Alzheimer's disease.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 17;16:1528919. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1528919. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40166467 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Natural anti-cancer products: insights from herbal medicine.Chin Med. 2025 Jun 9;20(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s13020-025-01124-y. Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40490812 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of acupuncture at the Taichong (LIV3) and Hegu (LI4) points on functional connectivity with the retrosplenial cortex in patients with Alzheimer's disease.Front Neurosci. 2025 Jan 14;18:1511183. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1511183. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39877657 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the therapeutic potential of natural products in Alzheimer's disease: insights from in vitro, in vivo, and clinical studies.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 23;16:1601712. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1601712. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40626308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acupuncture improves spatial learning and memory impairment caused by herpes simplex virus type-1 in rats through the p38 MAPK/CREB pathway.J Physiol Sci. 2024 Oct 3;74(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s12576-024-00941-4. J Physiol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39363248 Free PMC article.
-
Bryophyllum pinnatum (L.) Pers. Modulates Multiple Neuroprotective Targets in Alzheimer's Disease: Evidence from Computational and Experimental Validation.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Jul 19. doi: 10.1007/s12013-025-01832-0. Online ahead of print. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 40684044
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

