The combination of Tanshinone IIA and Astragaloside IV attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting the STING pathway
- PMID: 38419127
- PMCID: PMC10900662
- DOI: 10.1186/s13020-024-00908-y
The combination of Tanshinone IIA and Astragaloside IV attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting the STING pathway
Abstract
Background: Astragaloside IV (As-IV) and Tanshinone IIA (Ta-IIA) are the main ingredients of traditional Chinese medicinal Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bunge and Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge, respectively, both of which have been employed in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Nevertheless, the efficacy of the combination (Co) of Ta-IIA and As-IV for cardiovascular diseases remain unclear and warrant further investigation. This study aimed to investigate the efficacy and the underlying molecular mechanism of Co in treating myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury (MIRI).
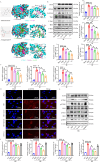
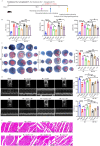
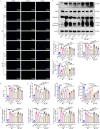
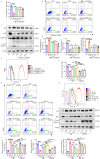
Methods: In order to assess the efficacy of Co, an in vivo MIRI mouse model was created by temporarily blocking the coronary arteries for 30 min and then releasing the blockage. Parameters such as blood myocardial enzymes, infarct size, and ventricular function were measured. Additionally, in vitro experiments were conducted using HL1 cells in both hypoxia-reoxygenation model and oxidative stress models. The apoptosis rate, expression levels of apoptosis-related proteins, oxidative stress indexes, and release of inflammatory factors were detected. Furthermore, molecular docking was applied to examine the binding properties of Ta-IIA and As-IV to STING, and western blotting was performed to analyze protein expression of the STING pathway. Additionally, the protective effect of Ta-IIA, As-IV and Co via inhibiting STING was further confirmed in models of knockdown STING by siRNA and adding STING agonist.
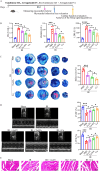
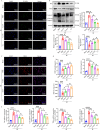
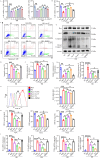
Results: Both in vitro and in vivo data demonstrated that, compared to Ta-IIA or As-IV alone, the Co exhibited superior efficacy in reducing the area of myocardial infarction, lowering myocardial enzyme levels, and promoting the recovery of myocardial contractility. Furthermore, the Co showed more potent anti-apoptosis, antioxidant, and anti-inflammation effects. Additionally, the Co enhanced the inhibitory effects of Ta-IIA and As-IV on STING phosphorylation and the activation of STING signaling pathway. However, the administration of a STING agonist attenuated the protective effects of the Co, Ta-IIA, and As-IV by compromising their anti-apoptotic, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory effects in MIRI.
Conclusion: Compared to the individual administration of Ta-IIA or As-IV, the combined treatment demonstrated more potent ability in inhibiting apoptosis, oxidative stress, inflammation, and the STING signaling pathway in the context of MIRI, indicating a more powerful protective effect against MIRI.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Astragaloside IV; Myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury; Oxidative stress; STING pathway; Tanshinone IIA.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of tanshinone IIA in rat models with myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: a systematic mini-review and meta-analysis.PeerJ. 2024 Aug 16;12:e17885. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17885. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39161965 Free PMC article.
-
Luteolin protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by reducing oxidative stress and apoptosis through the p53 pathway.J Integr Med. 2024 Nov;22(6):652-664. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2024.09.001. Epub 2024 Sep 7. J Integr Med. 2024. PMID: 39343710
-
Tanshinone IIA inhibits cardiomyocyte pyroptosis through TLR4/NF-κB p65 pathway after acute myocardial infarction.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Sep 12;11:1252942. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1252942. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37766966 Free PMC article.
-
Astragaloside IV prevents acute myocardial infarction by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway.J Food Biochem. 2021 Jul;45(7):e13757. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13757. Epub 2021 May 25. J Food Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34032295
-
The role of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Oct;123:110714. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110714. Epub 2023 Jul 29. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37523969 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring Astragaloside IV in Ischemic Heart Disease: A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Preclinical Cardiotoxicity Models.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2025 Jul;39(7):e70365. doi: 10.1002/jbt.70365. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40551496 Free PMC article.
-
Progress of cGAS-STING signaling pathway-based modulation of immune response by traditional Chinese medicine in clinical diseases.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 16;15:1510628. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1510628. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39737190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Qing-Xin-Jie-Yu Granule attenuates myocardial infarction-induced inflammatory response by regulating the MK2/TTP pathway.Pharm Biol. 2025 Dec;63(1):128-140. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2025.2467377. Epub 2025 Feb 21. Pharm Biol. 2025. PMID: 39980416 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic analysis of Tanshinone IIA's regulation of the ATM/GADD45/ORC signaling pathway to reduce myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Dec 24;15:1510380. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1510380. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39776578 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Natural Products in Diabetic Retinopathy.Biomedicines. 2024 May 21;12(6):1138. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12061138. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38927345 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

