Immune cell early activation, apoptotic kinetic, and T-cell functional impairment in domestic pigs after ASFV CADC_HN09 strain infection
- PMID: 38419627
- PMCID: PMC10899498
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1328177
Immune cell early activation, apoptotic kinetic, and T-cell functional impairment in domestic pigs after ASFV CADC_HN09 strain infection
Abstract
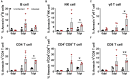
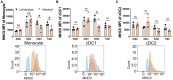
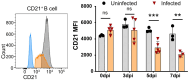
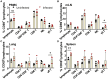
African swine fever (ASF) caused by the African swine fever virus (ASFV) is a fatal and highly contagious disease of domestic pigs characterized by rapid disease progression and death within 2 weeks. How the immune cells respond to acute ASFV infection and contribute to the immunopathogenesis of ASFV has not been completely understood. In this study, we examined the activation, apoptosis, and functional changes of distinct immune cells in domestic pigs following acute infection with the ASFV CADC_HN09 strain using multicolor flow cytometry. We found that ASFV infection induced broad apoptosis of DCs, monocytes, neutrophils, and lymphocytes in the peripheral blood of pigs over time. The expression of MHC class II molecule (SLA-DR/DQ) on monocytes and conventional DCs as well as CD21 expression on B cells were downregulated after ASFV infection, implying a potential impairment of antigen presentation and humoral response. Further examination of CD69 and ex vivo expression of IFN-γ on immune cells showed that T cells were transiently activated and expressed IFN-γ as early as 5 days post-infection. However, the capability of T cells to produce cytokines was significantly impaired in the infected pigs when stimulated with mitogen. These results suggest that the adaptive cellular immunity to ASFV might be initiated but later overridden by ASFV-induced immunosuppression. Our study clarified the cell types that were affected by ASFV infection and contributed to lymphopenia, improving our understanding of the immunopathogenesis of ASFV.
Keywords: ASFV; T cell early activation; apoptotic; cytokine; immunopathogenesis.
Copyright © 2024 Tian, Wang, He, Cao, Li, Jiang, Shi, Hao, Wei, Wang, Qie, Wang, Li, Hao, Zhu, Wu, Shang and Zhai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Carrasco L., Gómez-Villamandos J. C., Bautista M. J., Martín de las Mulas J., Villeda C. J., Wilkinson P. J., et al. . (1996b). In vivo replication of African swine fever virus (Malawi '83) in neutrophils. Vet. Res. 27, 55–62. PMID: - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

