Organoboron-thiophene-based polymer electrodes for high-performance lithium-ion batteries
- PMID: 38419680
- PMCID: PMC10901214
- DOI: 10.1039/d3ra06060h
Organoboron-thiophene-based polymer electrodes for high-performance lithium-ion batteries
Abstract
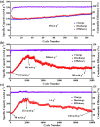
Polymer electrodes are drawing widespread attention to the future generation of lithium-ion battery materials. However, weak electrochemical performance of organic anode materials still exists, such as low capacity, low rate performance, and low cyclability. Herein, we successfully constructed a donor-acceptor thiophene-based polymer (PBT-1) by introducing an organoboron unit. The charge delocalization and lower LUMO energy level due to the unique structure enabled good performance in electrochemical tests with a reversible capacity of 405 mA h g-1 at 0.5 A g-1 and over 10 000 cycles at 1 A g-1. Moreover, electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectra revealed that the unique stable spin system in the PBT-1 backbone during cycling provides a fundamental explanation for the highly stable electrochemical performance. This work offers a reliable reference for the design of organic anode materials and expands the potential application directions of organoboron chemistry.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
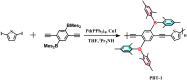



References
-
- Lu Y. Chen J. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2020;4:127–142. - PubMed
-
- Song Z. Zhou H. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013;6:2280–2301.
-
- Kaur R. Chhabra V. A. Chaudhary V. Vikrant K. Tripathi S. K. Su Y. Kumar P. Kim K.-H. Deep A. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022;46:13178–13204.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

