Transforming medicine: artificial intelligence integration in the peripheral nervous system
- PMID: 38419700
- PMCID: PMC10899496
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1332048
Transforming medicine: artificial intelligence integration in the peripheral nervous system
Abstract
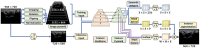
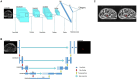
In recent years, artificial intelligence (AI) has undergone remarkable advancements, exerting a significant influence across a multitude of fields. One area that has particularly garnered attention and witnessed substantial progress is its integration into the realm of the nervous system. This article provides a comprehensive examination of AI's applications within the peripheral nervous system, with a specific focus on AI-enhanced diagnostics for peripheral nervous system disorders, AI-driven pain management, advancements in neuroprosthetics, and the development of neural network models. By illuminating these facets, we unveil the burgeoning opportunities for revolutionary medical interventions and the enhancement of human capabilities, thus paving the way for a future in which AI becomes an integral component of our nervous system's interface.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; neural network; neuro-prosthetic; pain management; peripheral nervous system.
Copyright © 2024 Qian, Alhaskawi, Dong, Ni, Abdalbary and Lu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
From Nanobots to Neural Networks: Multifaceted Revolution of Artificial Intelligence in Surgical Medicine and Therapeutics.Cureus. 2023 Nov 19;15(11):e49082. doi: 10.7759/cureus.49082. eCollection 2023 Nov. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38125253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmental resilience through artificial intelligence: innovations in monitoring and management.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024 Mar;31(12):18379-18395. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-32404-z. Epub 2024 Feb 15. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38358626 Review.
-
Mapping the Bibliometrics Landscape of AI in Medicine: Methodological Study.J Med Internet Res. 2023 Dec 8;25:e45815. doi: 10.2196/45815. J Med Internet Res. 2023. PMID: 38064255 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Mental Healthcare: Progress, Pitfalls, and Promises.Cureus. 2023 Sep 5;15(9):e44748. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44748. eCollection 2023 Sep. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37809254 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing head and neck tumor management with artificial intelligence: Integration and perspectives.Semin Cancer Biol. 2023 Oct;95:52-74. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2023.07.002. Epub 2023 Jul 18. Semin Cancer Biol. 2023. PMID: 37473825 Review.
Cited by
-
Artificial Intelligence and Neuroscience: Transformative Synergies in Brain Research and Clinical Applications.J Clin Med. 2025 Jan 16;14(2):550. doi: 10.3390/jcm14020550. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 39860555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of Screening Tests for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: An Umbrella Review.J Diabetes Res. 2024 Dec 4;2024:5902036. doi: 10.1155/jdr/5902036. eCollection 2024. J Diabetes Res. 2024. PMID: 39664106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques for predicting neuropathic pain in patients with cancer: A systematic review.Digit Health. 2025 Jul 7;11:20552076251358315. doi: 10.1177/20552076251358315. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2025. PMID: 40656844 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

