Case report: Exploring chemoradiotherapy-induced leukoencephalopathy with 7T imaging and quantitative susceptibility mapping
- PMID: 38419703
- PMCID: PMC10899325
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1362704
Case report: Exploring chemoradiotherapy-induced leukoencephalopathy with 7T imaging and quantitative susceptibility mapping
Abstract
Chemotherapy and radiotherapy are widely used in the treatment of central nervous system tumors and acute lymphocytic leukemia even in the pediatric population. However, such treatments run the risk of a broad spectrum of cognitive and neurological deficits. Even though the correlation with cognitive decline is still not clear, neuroradiological defects linked to white matter injury and vasculopathies may be identified. Thanks to the use of 7T MRI it is possible to better define the vascular pattern of the brain lesions with the added advantage of identifying their characteristics and anatomical localization, which, however, are not evident with a conventional brain scan. Moreover, the use of Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM) makes it possible to discriminate between calcium deposits on vessels (chemo-radiation-induced) and hemoglobin deposition in radio-induced cavernomas, speculating, as a result, about the pathophysiology of iatrogenic brain damage. We describe the case of a 9 year-old boy with a T-type acute lymphoid leukemia who had previously been treated with polychemotherapy and high-dose RT. To better define the child's neuroradiological pattern, 7T MRI and QSM were performed in addition to conventional imaging examinations. Our case report suggests the potential usefulness of a QSM study to distinguish radio-induced vascular malformations from mineralizing microangiopathy.
Keywords: 7 Tesla; brain damage; chemoradiotherapy; leukoencephalopathy; neurotoxicity; ultra-high field MRI.
Copyright © 2024 Celardo, Scaffei, Buchignani, Donatelli, Costagli, Cristofani, Canapicchi, Pasquariello, Tosetti, Battini and Biagi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
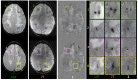
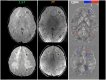
Similar articles
-
High-resolution characterisation of the aging brain using simultaneous quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) and R2* measurements at 7T.Neuroimage. 2016 Sep;138:43-63. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.05.024. Epub 2016 May 13. Neuroimage. 2016. PMID: 27181761
-
Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping of Amyloid-β Aggregates in Alzheimer's Disease with 7T MR.J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;64(2):393-404. doi: 10.3233/JAD-180118. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018. PMID: 29865069
-
Comparison of quantitative susceptibility mapping methods on evaluating radiation-induced cerebral microbleeds and basal ganglia at 3T and 7T.NMR Biomed. 2022 May;35(5):e4666. doi: 10.1002/nbm.4666. Epub 2022 Jan 24. NMR Biomed. 2022. PMID: 35075701 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term sequelae of cancer treatment on the central nervous system in childhood.Med Pediatr Oncol. 1987;15(5):241-53. doi: 10.1002/mpo.2950150505. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1987. PMID: 3309606 Review.
-
Patents on Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM) of Tissue Magnetism.Recent Pat Biotechnol. 2019;13(2):90-113. doi: 10.2174/1872208313666181217112745. Recent Pat Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30556508 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

