Sarcopenic Obesity as a Risk Factor for Cardiovascular Disease: An Underrecognized Clinical Entity
- PMID: 38419720
- PMCID: PMC10897945
- DOI: 10.17925/HI.2023.17.2.6
Sarcopenic Obesity as a Risk Factor for Cardiovascular Disease: An Underrecognized Clinical Entity
Abstract
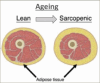
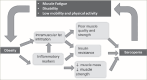
Sarcopenic obesity (SO) is a chronic condition and an emerging health challenge, in view of the growing elderly population and the obesity epidemic. Due to a lack of awareness among treating doctors and the non-specific nauture of the associated symptoms, SO remains grossly underdiagnosed. There is no consensus yet on a standard definition or diagnostic criteria for SO, which limits the estimation of the global prevalence of this condition. It has been linked to numerous metabolic derangements, cardiovascular disease (CVD) and mortality. The treatment of SO is multimodal and requires expertise across multiple specialties. While dietary modifications and exercise regimens have shown a potential therapeutic benefit, there is currently no proven pharmacological management for SO. However, numerous drugs and the role of bariatric surgery are still under trial, and have great scope for further research. This article covers the available literature regarding the definition, diagnostic criteria, and prevalence of SO, with available evidence linking it to CVD, metabolic disease and mortality, and an overview of current directives on management.
Keywords: Aging; lifestyle; muscle; obesity; sarcopenia; sarcopenic obesity.
© Touch Medical Media 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: Aditya John Binu, Nitin Kapoor, Saptarshi Bhattacharya, Kamal Kishor and Sanjay Kalra have no financial or non-financial relationships or activities to declare in relation to this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sarcopenic obesity as a determinant of cardiovascular disease risk in older people: a systematic review.Postgrad Med. 2021 Nov;133(8):831-842. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2021.1942934. Epub 2021 Jul 12. Postgrad Med. 2021. PMID: 34126036
-
Sarcopenic obesity.Hormones (Athens). 2018 Sep;17(3):321-331. doi: 10.1007/s42000-018-0049-x. Epub 2018 Jul 16. Hormones (Athens). 2018. PMID: 30014320 Review.
-
Sarcopenic Obesity: Time to Meet the Challenge.Obes Facts. 2018;11(4):294-305. doi: 10.1159/000490361. Epub 2018 Jul 18. Obes Facts. 2018. PMID: 30016792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sarcopenic obesity: Time to meet the challenge.Clin Nutr. 2018 Dec;37(6 Pt A):1787-1793. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2018.04.018. Epub 2018 May 7. Clin Nutr. 2018. PMID: 29857921
-
Critical appraisal of definitions and diagnostic criteria for sarcopenic obesity based on a systematic review.Clin Nutr. 2020 Aug;39(8):2368-2388. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2019.11.024. Epub 2019 Nov 27. Clin Nutr. 2020. PMID: 31813698
References
-
- Peterson PG. Gray dawn: The global aging crisis. Foreign Aff. 1999;78:42. doi: 10.2307/20020238. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources