Three-dimensional array of microbubbles sonoporation of cells in microfluidics
- PMID: 38419723
- PMCID: PMC10899490
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1353333
Three-dimensional array of microbubbles sonoporation of cells in microfluidics
Abstract
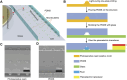
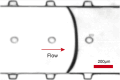
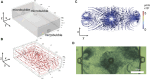
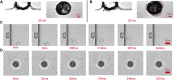
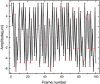
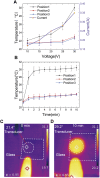
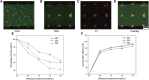
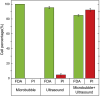
Sonoporation is a popular membrane disruption technique widely applicable in various fields, including cell therapy, drug delivery, and biomanufacturing. In recent years, there has been significant progress in achieving controlled, high-viability, and high-efficiency cell sonoporation in microfluidics. If the microchannels are too small, especially when scaled down to the cellular level, it still remains a challenge to overcome microchannel clogging, and low throughput. Here, we presented a microfluidic device capable of modulating membrane permeability through oscillating three-dimensional array of microbubbles. Simulations were performed to analyze the effective range of action of the oscillating microbubbles to obtain the optimal microchannel size. Utilizing a high-precision light curing 3D printer to fabricate uniformly sized microstructures in a one-step on both the side walls and the top surface for the generation of microbubbles. These microbubbles oscillated with nearly identical amplitudes and frequencies, ensuring efficient and stable sonoporation within the system. Cells were captured and trapped on the bubble surface by the acoustic streaming and secondary acoustic radiation forces induced by the oscillating microbubbles. At a driving voltage of 30 Vpp, the sonoporation efficiency of cells reached 93.9% ± 2.4%.
Keywords: acoustic radiation force; acoustic streaming; membrane disruption; microfluidics; sonoporation.
Copyright © 2024 Huang, Lin, Liu, Wu, Chen, Zhu, You and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sonoporation of Cells by a Parallel Stable Cavitation Microbubble Array.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019 Jun 17;6(17):1900557. doi: 10.1002/advs.201900557. eCollection 2019 Sep 4. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019. PMID: 31508275 Free PMC article.
-
Control of Acoustic Cavitation for Efficient Sonoporation with Phase-Shift Nanoemulsions.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2019 Mar;45(3):846-858. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2018.12.001. Epub 2019 Jan 11. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 30638968 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound Imaging of Microbubble Activity during Sonoporation Pulse Sequences.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2019 Mar;45(3):833-845. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2018.11.011. Epub 2019 Jan 9. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 30638695 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms underlying sonoporation: Interaction between microbubbles and cells.Ultrason Sonochem. 2020 Oct;67:105096. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105096. Epub 2020 Mar 26. Ultrason Sonochem. 2020. PMID: 32278246 Review.
-
Ultrasound and microbubble mediated therapeutic delivery: Underlying mechanisms and future outlook.J Control Release. 2020 Oct 10;326:75-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.06.008. Epub 2020 Jun 14. J Control Release. 2020. PMID: 32554041 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

