Loss of NSD2 causes dysregulation of synaptic genes and altered H3K36 dimethylation in mice
- PMID: 38419783
- PMCID: PMC10899350
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1308234
Loss of NSD2 causes dysregulation of synaptic genes and altered H3K36 dimethylation in mice
Abstract
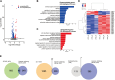
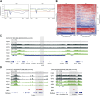
Background: Epigenetic disruptions have been implicated in neurodevelopmental disorders. NSD2 is associated with developmental delay/intellectual disability; however, its role in brain development and function remains unclear. Methods: We performed transcriptomic and epigenetic analyses using Nsd2 knockout mice to better understand the role of NSD2 in the brain. Results and discussion: Transcriptomic analysis revealed that the loss of NSD2 caused dysregulation of genes related to synaptic transmission and formation. By analyzing changes in H3 lysine 36 dimethylation (H3K36me2), NSD2-mediated H3K36me2 mainly marked quiescent state regions and the redistribution of H3K36me2 occurred at transcribed genes and enhancers. By integrating transcriptomic and epigenetic data, we observed that H3K36me2 changes in a subset of dysregulated genes related to synaptic transmission and formation. These results suggest that NSD2 is involved in the regulation of genes important for neural function through H3K36me2. Our findings provide insights into the role of NSD2 and improve our understanding of epigenetic regulation in the brain.
Keywords: ChIP sequencing; H3K36me2; NSD2; RNA sequencing; neurodevelopmental disorder.
Copyright © 2024 Kinoshita, Kojima, Ohnishi, Takayama, Kikuchi, Takada, Nakabayashi, Kawai and Hata.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A PWWP Domain of Histone-Lysine N-Methyltransferase NSD2 Binds to Dimethylated Lys-36 of Histone H3 and Regulates NSD2 Function at Chromatin.J Biol Chem. 2016 Apr 15;291(16):8465-74. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.720748. Epub 2016 Feb 24. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26912663 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased NSD2 impairs stromal cell proliferation in human endometrium via reprogramming H3K36me2.Reproduction. 2024 Feb 12;167(3):e230254. doi: 10.1530/REP-23-0254. Print 2024 Mar 1. Reproduction. 2024. PMID: 38236723 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic perturbations of SETD2, NSD1, NSD2, NSD3 and ASH1L reveals their distinct contributions to H3K36 methylation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Oct 18:2023.09.27.559313. doi: 10.1101/2023.09.27.559313. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Genome Biol. 2024 Oct 10;25(1):263. doi: 10.1186/s13059-024-03415-3. PMID: 37905045 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
NSD2 as a Promising Target in Hematological Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 21;23(19):11075. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911075. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug Discovery Targeting Nuclear Receptor Binding SET Domain Protein 2 (NSD2).J Med Chem. 2023 Aug 24;66(16):10991-11026. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00948. Epub 2023 Aug 14. J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37578463 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chromatin modifiers in neurodevelopment.Front Mol Neurosci. 2025 May 21;18:1551107. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2025.1551107. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40469903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loss-of-function mutation of NSD2 is associated with abnormal placentation accompanied by fetal growth retardation in mice.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 21;20(7):e0328243. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0328243. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40690504 Free PMC article.
-
A Computational Approach to Identify Novel Protein Targets Uncovers New Potential Mechanisms of Action of Mirtazapine S(+) and R(-) Enantiomers in Rett Syndrome.J Neurochem. 2025 May;169(5):e70093. doi: 10.1111/jnc.70093. J Neurochem. 2025. PMID: 40417780 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balan S., Iwayama Y., Ohnishi T., Fukuda M., Shirai A., Yamada A., et al. (2021). A loss-of-function variant in SUV39H2 identified in autism-spectrum disorder causes altered H3K9 trimethylation and dysregulation of protocadherin β-cluster genes in the developing brain. Mol. Psychiatry 26, 7550–7559. 10.1038/s41380-021-01199-7 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

