Molecular diversity and functional dynamics in the central amygdala
- PMID: 38419794
- PMCID: PMC10899328
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1364268
Molecular diversity and functional dynamics in the central amygdala
Abstract
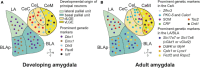
The central amygdala (CeA) is crucial in integrating sensory and associative information to mediate adaptive responses to emotional stimuli. Recent advances in genetic techniques like optogenetics and chemogenetics have deepened our understanding of distinct neuronal populations within the CeA, particularly those involved in fear learning and memory consolidation. However, challenges remain due to overlapping genetic markers complicating neuron identification. Furthermore, a comprehensive understanding of molecularly defined cell types and their projection patterns, which are essential for elucidating functional roles, is still developing. Recent advancements in transcriptomics are starting to bridge these gaps, offering new insights into the functional dynamics of CeA neurons. In this review, we provide an overview of the expanding genetic markers for amygdala research, encompassing recent developments and current trends. We also discuss how novel transcriptomic approaches are redefining cell types in the CeA and setting the stage for comprehensive functional studies.
Keywords: amygdala; cell types; fear learning; memory; transcriptomics.
Copyright © 2024 Yeh, Zuo and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multimodal mapping of cell types and projections in the central nucleus of the amygdala.Elife. 2023 Jan 20;12:e84262. doi: 10.7554/eLife.84262. Elife. 2023. PMID: 36661218 Free PMC article.
-
Central Amygdala Somatostatin Neurons Gate Passive and Active Defensive Behaviors.J Neurosci. 2016 Jun 15;36(24):6488-96. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4419-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27307236 Free PMC article.
-
A Central Amygdala-Globus Pallidus Circuit Conveys Unconditioned Stimulus-Related Information and Controls Fear Learning.J Neurosci. 2020 Nov 18;40(47):9043-9054. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2090-20.2020. Epub 2020 Oct 16. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33067362 Free PMC article.
-
Amygdala Inhibitory Circuits Regulate Associative Fear Conditioning.Biol Psychiatry. 2018 May 15;83(10):800-809. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.10.006. Epub 2017 Oct 14. Biol Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29174478 Review.
-
Synaptic encoding of fear memories in the amygdala.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2019 Feb;54:54-59. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2018.08.012. Epub 2018 Sep 11. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30216780 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Astrocytes in Rodent Anxiety-Related Behavior: Role of Calcium and Beyond.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 19;26(6):2774. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062774. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Galactooligosaccharides Attenuate Behavioural, Haematological and Immunological Abnormalities and Influence Gut Microbiota in Rats with Amygdala Hyperactivation Induced by Electrical Stimulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 3;26(9):4353. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094353. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362590 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asok A., Draper A., Hoffman A. F., Schulkin J., Lupica C. R., Rosen J. B. (2018). Optogenetic silencing of a corticotropin-releasing factor pathway from the central amygdala to the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis disrupts sustained fear. Mol. Psychiatry 23 914–922. 10.1038/mp.2017.79 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

