Tetrandrine alleviates oxaliplatin-induced mechanical allodynia via modulation of inflammation-related genes
- PMID: 38419796
- PMCID: PMC10899404
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1333842
Tetrandrine alleviates oxaliplatin-induced mechanical allodynia via modulation of inflammation-related genes
Abstract
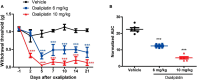
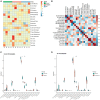
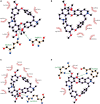
Oxaliplatin, a platinum-based chemotherapy drug, causes neuropathic pain, yet effective pharmacological treatments are lacking. Previously, we showed that tetrandrine (TET), with anti-inflammatory properties, reduces mechanical allodynia in nerve-injured mice. This study explores the effect of TET on oxaliplatin-induced mechanical allodynia and gene changes in mice. Male C57BL/6J mice received oxaliplatin intraperitoneally to induce mechanical allodynia. Post-treatment with TET or vehicle, the mechanical withdrawal threshold (WMT) was assessed using von Frey filaments. TET alleviated oxaliplatin-induced mechanical allodynia. RNA sequencing identified 365 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the Control vs. Oxaliplatin group and 229 DEGs in the Oxaliplatin vs. TET group. Pearson correlation analysis of co-regulated DEGs and inflammation-related genes (IRGs) revealed 104 co-regulated inflammation-related genes (Co-IRGs) (|cor| > 0.8, P < 0.01). The top 30 genes in the PPI network were identified. Arg2, Cxcl12, H2-Q6, Kdr, and Nfkbia were highlighted based on ROC analysis. Subsequently, Arg2, Cxcl12, Kdr, and Nfkbia were further verified by qRCR. Immune infiltration analysis indicated increased follicular CD4 T cell infiltration in oxaliplatin-treated mice, reduced by TET. Molecular docking showed strong binding affinity between TET and proteins encoded by Arg2, Cxcl12, Kdr, and Nfkbia. In summary, TET may alleviate oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy in clinical conditions.
Keywords: RNA-Seq; inflammation; mechanical allodynia; molecular docking; oxaliplatin; tetrandrine.
Copyright © 2024 Zhang, Wu, Liu, Chen and Zhai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Tetrandrine attenuates SNI-induced mechanical allodynia by inhibiting spinal CKLF1.Neuropharmacology. 2023 Nov 1;238:109673. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2023.109673. Epub 2023 Jul 28. Neuropharmacology. 2023. PMID: 37517461
-
Differential pharmacological alleviation of oxaliplatin-induced hyperalgesia/allodynia at cephalic versus extra-cephalic level in rodents.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Apr;79:432-43. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.12.011. Epub 2013 Dec 19. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24361454
-
Clonidine, an alpha-2 adrenoceptor agonist relieves mechanical allodynia in oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic mice; potentiation by spinal p38 MAPK inhibition without motor dysfunction and hypotension.Int J Cancer. 2016 May 15;138(10):2466-76. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29980. Epub 2016 Jan 11. Int J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26704560
-
Anti-allodynic effect of Buja in a rat model of oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy via spinal astrocytes and pro-inflammatory cytokines suppression.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Jan 14;17(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1556-z. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28088201 Free PMC article.
-
The α9α10 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Antagonist αO-Conotoxin GeXIVA[1,2] Alleviates and Reverses Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathic Pain.Mar Drugs. 2019 May 5;17(5):265. doi: 10.3390/md17050265. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31060282 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abd-Elmawla M., Abdelalim E., Ahmed K., Rizk S. (2023). The neuroprotective effect of pterostilbene on oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy via its anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative and anti-apoptotic effects: Comparative study with celecoxib. Life Sci. 315:121364. 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.121364 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

