Orexin and cannabinoid systems modulate long-term potentiation of the hippocampus CA1 area in anesthetized rats
- PMID: 38419882
- PMCID: PMC10897562
- DOI: 10.22038/IJBMS.2023.73979.16075
Orexin and cannabinoid systems modulate long-term potentiation of the hippocampus CA1 area in anesthetized rats
Abstract
Objectives: Long-term potentiation (LTP) is a kind of synaptic plasticity and has a key role in learning and memory. Endocannabinoids and orexins are the endogenous systems that can modulate synaptic plasticity. Given that new studies have shown an interaction between cannabinoid and orexin systems in the brain, we decided to examine this interaction between the two systems on LTP induction in rat's hippocampus.
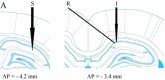
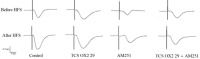
Materials and methods: Twenty-eight male Wistar rats were used for evaluating the effects of co-administrating of cannabinoid-1 receptor (CB1R) antagonist (AM251) and orexin-2 receptor (OX2R) antagonist (TCS OX2 29) on the induction of LTP in the Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapses of rat hippocampus. The drugs were microinjected into the CA1 area of rat hippocampus 30 min before inducing of LTP.
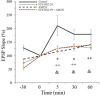
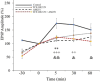
Results: Results showed that sole administration of the antagonists inhibited LTP, with respect to the control group. Also, co-administrating of them reduced LTP as compared to the control group, but not significantly more than that when the antagonists were solely microinjected into the CA1. Nonetheless, the inhibitory effect of concurrent administration of the antagonists on LTP lasted until the end of the recording.
Conclusion: These results propose that endogenous cannabinoids and orexins play a role in the expression of LTP, at least by CA1-CB1Rs and CA1-OX2Rs, respectively. Finally, there is no interaction between CB1R and OX2R on the induction of LTP in the Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapses; therefore, these two systems possibly act through common signaling pathways in the hippocampus's CA1 region.
Keywords: AM251; Cannabinoid receptors; Hippocampus; Long-term potentiation; Orexin receptors; TCS OX2 29.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare there are no conflicts of interest in this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Orexin A induces bidirectional modulation of synaptic plasticity: Inhibiting long-term potentiation and preventing depotentiation.Neuropharmacology. 2016 Aug;107:168-180. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.03.005. Epub 2016 Mar 7. Neuropharmacology. 2016. PMID: 26965217
-
The Effect of Orexin-2 and Endocannabinoid-1 Antagonists on Neuronal Activity of Hippocampal CA1 Pyramidal Neurons in Response to Tramadol in Rats.Adv Biomed Res. 2022 Mar 30;11:26. doi: 10.4103/abr.abr_65_21. eCollection 2022. Adv Biomed Res. 2022. PMID: 35720213 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of selective orexin receptor-2 and cannabinoid receptor-1 antagonists on the response of medial prefrontal cortex neurons to tramadol.Synapse. 2022 Jun;76(7-8):e22232. doi: 10.1002/syn.22232. Epub 2022 Mar 29. Synapse. 2022. PMID: 35313383
-
The interactive role of CB1 receptors and L-type calcium channels in hippocampal long-term potentiation in rats.Brain Res Bull. 2017 May;131:168-175. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2017.04.009. Epub 2017 Apr 23. Brain Res Bull. 2017. PMID: 28442324
-
Activation of Group II Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors Promotes LTP Induction at Schaffer Collateral-CA1 Pyramidal Cell Synapses by Priming NMDA Receptors.J Neurosci. 2016 Nov 9;36(45):11521-11531. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1519-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27911756 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bliss TV, Collingridge GL. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993;361:31–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
