Exploring the psychometric properties of Gujarati version of WHOQOL-BREF scale among general population of Western Gujarat: A confirmatory factor analysis
- PMID: 38419931
- PMCID: PMC10898523
- DOI: 10.4103/indianjpsychiatry.indianjpsychiatry_391_23
Exploring the psychometric properties of Gujarati version of WHOQOL-BREF scale among general population of Western Gujarat: A confirmatory factor analysis
Abstract
Background: Quality of life (QOL) is a useful component in assessing the health of people and society. There are many reports on the validity of the four-domain structure of the World Health Organization Quality of Life-BREF (WHOQOL-BREF), but few studies have investigated the possibility of a better alternative model fit among the general population.
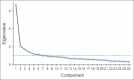
Objective: The objectives of the study were to perform exploratory factor analysis (EFA) and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) using the WHOQOL-BREF and to generate a model that fits among the general population of western Gujarat.
Materials and methods: A community-based cross-sectional study was conducted from September 2022 to February 2023 using the Gujarati version of the WHOQOL-BREF questionnaire among the general population of urban and rural areas. Factor analysis was performed to check the model fit.
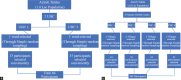
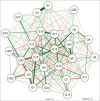
Results: Factor analysis gave a five-factor structure, and the CFA suggested that the model was acceptable.
Conclusion: Based on the findings, this model can better explain QOL and can be used as a reliable and valid instrument for evaluating QOL in the general population of Gujarat.
Keywords: Confirmatory factor analysis; Gujarat; WHOQOL BREF; factor analysis; general population.
Copyright: © 2024 Indian Journal of Psychiatry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Validation and reliability of the Abbreviated World Health Organization Quality of Life Instrument (WHOQOL-BREF) in the hospitalized trauma population.Injury. 2018 Oct;49(10):1796-1804. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2018.08.016. Epub 2018 Aug 23. Injury. 2018. PMID: 30154022
-
Psychometric evaluation of the WHOQOL-BREF and its shorter versions for general Thai population: confirmatory factor analysis and Rasch analysis.Qual Life Res. 2024 Feb;33(2):335-348. doi: 10.1007/s11136-023-03521-y. Epub 2023 Oct 31. Qual Life Res. 2024. PMID: 37906345
-
Quality of life in Vietnamese young adults: A validation analysis of the World Health Organization's quality of life (WHOQOL-BREF) instrument.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Dec 20;13:968771. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.968771. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36606129 Free PMC article.
-
Confirmatory factor analytical study of the WHOQOL-Bref: experience with Sudanese general population and psychiatric samples.BMC Med Res Methodol. 2007 Aug 1;7:37. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-7-37. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2007. PMID: 17678527 Free PMC article.
-
Psychometric properties of the Chinese version of the WHOQOL-HIV BREF to assess quality of life among people living with HIV/AIDS: a cross-sectional study.BMJ Open. 2017 Aug 21;7(8):e016382. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016382. BMJ Open. 2017. PMID: 28827253 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO-BREF . Geneva: 1996. Introduction, administration, scoring and generic version of the assessment.
-
- Min SK, Kim KI, Lee CI, Jung YC, Suh SY, Kim DK. Development of the Korean versions of WHO quality of life scale and WHOQOL-BREF. Qual Life Res. 2002;11:593–600. - PubMed
-
- Wong FY, Yang L, Yuen JWM, Chang KKP, Wong FKY. Assessing quality of life using WHOQOL-BREF: A cross-sectional study on the association between quality of life and neighborhood environmental satisfaction, and the mediating effect of health-related behaviors. BMC Public Health. 2018;18:1113. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Apidechkul T. Comparison of quality of life and mental health among elderly people in rural and suburban areas, Thailand. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2011;42:1282–92. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
