Analysis of survival rate and persistence predictors of baricitinib in real-world data from a large cohort of rheumatoid arthritis patients
- PMID: 38419949
- PMCID: PMC10899020
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crphar.2024.100178
Analysis of survival rate and persistence predictors of baricitinib in real-world data from a large cohort of rheumatoid arthritis patients
Abstract
Objectives: The persistence in therapy of rheumatoid arthritis drugs and particularly bDMARD is a limiting factor for their long-term use. The randomized controlled trials (RCTs) may not reflect real-world contexts due to strict inclusion and exclusion criteria. Baricitinib, which targets both JAK1 and JAK2, has been used in Italy for several years. The aim of this multi-center study is to assess the real world persistence on therapy of baricitinib in RA patients and to identify predictive factors of baricitinib's survival rate.
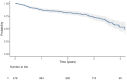
Methods: This is a retrospective, multicentric, Italian, longitudinal study. All patients were enrolled according to the following criteria: a) age ≥ 18 years old; b) diagnosed with RA according 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria; c) treated with baricitinib. In order to describe baricitinib clinical efficacy, the survival rate was evaluated by The Kaplan-Meier curve. Then, predictive factors of drug retention rate were assessed by performing the Cox analysis, identifying which risk factors influenced treatment persistence.
Results: Overall, we included 478 patients treated with baricitinib. Among them, 380 (79.5%) were females. Baricitinib's survival rate was 94.6% at 6 months, 87.9% at 12 months, 81.7% at 24 months and 53.4% at 48 months. The Cox analysis regression showed that a higher bDMARDs/tsDMARD line of therapy seems to be a negative prognostic factor for the drug retention rate (HR 1.26 CI 95% 1.07-1.49, p = 0.006.
Conclusion: Real-life study confirms baricitinib effectiveness up to 4 years, but previous treatment with bDMARDs was a negative prognostic factor for its survival rate.
Keywords: Baricitinib; Comorbidity; JAK inhibitors; Line of treatment; Prognostic factor; Real world; Rheumatoid arthritis; Survival rate; bDMARD; tsDMARD.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Choy E.H., Miceli-Richard C., Gonzalez-Gay M.A., et al. The effect of jak1/jak2 inhibition in rheumatoid arthritis: efficacy and safety of baricitinib. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2019;7:694–704. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous