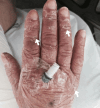
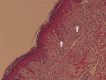
Dipyrone (Metamizole)-Induced Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
- PMID: 38420072
- PMCID: PMC10899118
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.53122
Dipyrone (Metamizole)-Induced Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
Abstract
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), a severe mucocutaneous hypersensitivity reaction primarily triggered by drugs, poses a low-incidence, high-mortality challenge. This report explores its clinical nuances and emphasizes supportive care as the mainstay of treatment. A 74-year-old female, burdened with a complex medical history, presented with a non-pruritic macular rash escalating to skin and oral mucosal involvement. A recent introduction of dipyrone (metamizole) implicated drug-induced SJS. Histopathological confirmation guided treatment involving supportive care, corticosteroids, and wound care, resulting in clinical improvement. The case underscores the significance of histopathological confirmation and thorough medication history in navigating SJS complexities, especially in patients with comorbidities like connective tissue disease. A successful multidisciplinary approach and the decision for post-discharge monitoring highlight the intricate management challenges. This case illuminates the intricate interplay of medication-induced hypersensitivity, comorbidities, and management challenges in SJS. Optimal outcomes require prompt diagnosis, trigger identification, and a multidisciplinary treatment approach, emphasizing ongoing research and clinical vigilance.
Keywords: adverse reactions; drug-induced allergic response; metamizole; rare skin disease; stevens-johnson-syndrome.
Copyright © 2024, Gomes Ferreira et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reaction to Lamotrigine: A Case of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome in a Psychiatric Patient.Cureus. 2025 Feb 10;17(2):e78812. doi: 10.7759/cureus.78812. eCollection 2025 Feb. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40078262 Free PMC article.
-
Current Perspectives on Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018 Feb;54(1):147-176. doi: 10.1007/s12016-017-8654-z. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29188475 Review.
-
A young female's battle with toxic epidermal necrolysis induced by NSAIDs: a case report.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024 Sep 30;86(11):6869-6873. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000002625. eCollection 2024 Nov. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39525738 Free PMC article.
-
Severe Hypersensitivity Reactions with Oral Manifestations: Case Reports on Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and DRESS Syndrome.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2024 Dec;16(Suppl 5):S4935-S4939. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_1090_24. Epub 2025 Jan 30. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2024. PMID: 40061645 Free PMC article.
-
Lamotrigine and Stevens-Johnson Syndrome Prevention.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2021 Mar 16;51(2):96-114. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2021. PMID: 34092825 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: A 15-year Regional Burn Center Experience.JPRAS Open. 2025 Feb 8;44:83-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jpra.2025.02.003. eCollection 2025 Jun. JPRAS Open. 2025. PMID: 40143959 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiological Characteristics and Prognostic Scoring in Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson Syndrome: Insights from a 17-Year Burn Center Experience.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Jan 3;61(1):66. doi: 10.3390/medicina61010066. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 39859048 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Current perspectives on Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Lerch M, Mainetti C, Terziroli Beretta-Piccoli B, Harr T. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018;54:147–176. - PubMed
-
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in patients with lupus erythematosus: a descriptive study of 17 cases from a national registry and review of the literature. Ziemer M, Kardaun SH, Liss Y, Mockenhaupt M. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:575–600. - PubMed
-
- Comprehensive survival analysis of a cohort of patients with Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Sekula P, Dunant A, Mockenhaupt M, et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133:1197–1204. - PubMed
-
- Severe cutaneous adverse reactions to drugs. Duong TA, Valeyrie-Allanore L, Wolkenstein P, Chosidow O. Lancet. 2017;390:1996–2011. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources