Adrenaline, Takotsubo, Anaphylaxis, and Kounis Syndrome (ATAK) Complex Unveiled: Integrating Takotsubo and Kounis Syndromes in the Context of Chemotherapy-Related Anaphylaxis
- PMID: 38420090
- PMCID: PMC10900278
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.53145
Adrenaline, Takotsubo, Anaphylaxis, and Kounis Syndrome (ATAK) Complex Unveiled: Integrating Takotsubo and Kounis Syndromes in the Context of Chemotherapy-Related Anaphylaxis
Abstract
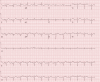
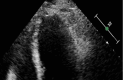
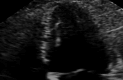
The convergence of takotsubo and Kounis syndromes, collectively referred to as the "ATAK complex" (short for adrenaline, takotsubo, anaphylaxis, and Kounis syndrome), poses a unique and challenging clinical scenario, especially in the context of chemotherapy-related anaphylaxis. We present a case report involving a 63-year-old woman undergoing chemotherapy for endometrial adenocarcinoma who experienced anaphylactic symptoms during treatment. Immediate administration of epinephrine was followed by the emergence of ST elevation, a reduced left ventricular ejection fraction, and wall motion abnormalities indicative of stress-induced cardiomyopathy. Detailed investigations revealed normal coronary arteries, prompting further exploration into the intricacies of the ATAK complex. Notably, the administration of intravenous rather than intramuscular epinephrine was identified as a contributing factor. This case underscores the critical importance of recognizing and managing the ATAK complex promptly, emphasizing the need for refined diagnostic and treatment guidelines. The interplay between adrenaline, takotsubo, anaphylaxis, and Kounis syndrome necessitates a nuanced approach, urging healthcare professionals to exercise caution and adhere to recommended administration routes. Increased awareness of the ATAK complex is imperative for optimizing patient outcomes and guiding therapeutic interventions in similar clinical scenarios. Further research is warranted to elucidate the underlying mechanisms and refine strategies for the effective management of this intricate syndrome.
Keywords: allergic angina; allergy; atak syndrome; coronary hypersensitivity disorder; kounis case study; st elevation mi.
Copyright © 2024, Puri et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ATAK Complex (Adrenaline, Takotsubo, Anaphylaxis, and Kounis Hypersensitivity-Associated Coronary Syndrome) after COVID-19 Vaccination and Review of the Literature.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Jan 31;11(2):322. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11020322. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36851200 Free PMC article.
-
ATAK complex (adrenaline, takotsubo, anaphylaxis, and kounis hypersensitivity-associated coronary syndrome) related to latamoxef administration-a case report.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Jul 22;11:1383903. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1383903. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39108674 Free PMC article.
-
Takotsubo cardiomyopathy associated with Kounis syndrome: A clinical case of the "ATAK complex".J Cardiol Cases. 2019 May 1;20(2):52-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jccase.2019.03.007. eCollection 2019 Aug. J Cardiol Cases. 2019. PMID: 31440312 Free PMC article.
-
Is Adrenaline Always the First Choice Therapy of Anaphylaxis? An Allergist-cardiologist Interdisciplinary Point of View.Curr Pharm Des. 2023;29(32):2545-2551. doi: 10.2174/0113816128257514231019165809. Curr Pharm Des. 2023. PMID: 37877509 Review.
-
The allergic myocardial infarction dilemma: is it the anaphylaxis or the epinephrine?J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2021 Oct;52(3):941-948. doi: 10.1007/s11239-021-02389-4. Epub 2021 Feb 5. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2021. PMID: 33544285 Review.
Cited by
-
Cardio-Oncoimmunology: Cardiac Toxicity, Cardiovascular Hypersensitivity, and Kounis Syndrome.Life (Basel). 2024 Mar 18;14(3):400. doi: 10.3390/life14030400. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38541723 Free PMC article.
-
Paclitaxel-related type I Kounis Syndrome in a very young patient with HER2-positive breast cancer and the role of genomics to disentangle a complex therapeutic scenario: a case report and narrative review.Breast. 2025 Jun;81:104465. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2025.104465. Epub 2025 Apr 4. Breast. 2025. PMID: 40199689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A rare case report of catecholamine-induced takotsubo in a patient with anaphylaxis shock due to amoxicillin-clavulanate.Turk J Emerg Med. 2025 Apr 1;25(2):152-155. doi: 10.4103/tjem.tjem_180_24. eCollection 2025 Apr-Jun. Turk J Emerg Med. 2025. PMID: 40248466 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources