Immediate effects of passion fruit juice supplementation on working ability and attention in healthy participants
- PMID: 38420135
- PMCID: PMC10899059
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crphys.2024.100120
Immediate effects of passion fruit juice supplementation on working ability and attention in healthy participants
Abstract
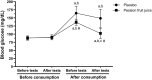
This study investigated the effects of a single consumption of passion fruit juice (PFJ) on working ability and attention. It included 14 healthy participants aged 20-30 years. Participants randomly consumed either placebo or 50% PFJ at 3.5 mL/kg body mass. Each intervention was divided into two phases (before and after consumption). Before consumption, the participants underwent blood glucose, blood pressure, and heart rate examinations. Then, working ability and attention were evaluated. Thereafter, the blood glucose, blood pressure, and heart rate were repeatedly examined. Next, the participants completed consumption. After consumption, the participants underwent the same experiments performed before consumption. The total working ability scores after consumption were significantly high in both interventions (P < 0.05). However, PFJ intervention had a significantly higher working ability at 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 min than placebo intervention (P < 0.05). Moreover, PFJ intervention had greater increases in attention than placebo intervention. There were no significant differences in attention between two interventions. The blood glucose levels were significantly lower in PFJ intervention than in placebo intervention both before the working ability test and after the attention test (P < 0.05). A single consumption of PFJ improved working ability in healthy participants. This may be enhanced by improving attentional focus and maintaining postprandial blood glucose.
Keywords: Blood glucose; Brain health; Executive function; Passion fruit.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Afkhami-Ardekani M., Shojaoddiny-Ardekani A. Effect of vitamin C on blood glucose, serum lipids & serum insulin in type 2 diabetes patients. Indian J. Med. Res. 2007;126(5):471–474. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

