Comparison of the efficacy of steroid-free versus classic steroid-containing regimens in primary membranous nephropathy
- PMID: 38420195
- PMCID: PMC10899500
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1286422
Comparison of the efficacy of steroid-free versus classic steroid-containing regimens in primary membranous nephropathy
Abstract
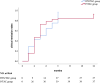
Objective: To compare the efficacy of a steroid-free regimen with steroid-based treatment in managing primary membranous nephropathy (PMN) and investigate the potential benefits of steroid-free regimens in PMN therapy. Methods: This was a single-centre prospective cohort study. A total of 81 patients were divided into two groups according to their medication regimen: a rituximab (RTX)/tacrolimus (TAC) group (low-dose RTX combined with low-dose TAC group, without steroids, n = 31) and a prednisone (P)/TAC group (P combined with TAC group, n = 61). The changes in 24-h urine protein quantification, levels of blood albumin, blood creatinine, total cholesterol, triglyceride and fasting blood glucose as well as anti-phospholipase A2 receptor antibody titres were observed in both groups before treatment and after 1, 3, 6 and 12 months of treatment. Clinical remission (complete and partial remission), serological remission and recurrence were assessed in both groups after treatment, and the occurrence of adverse reactions was observed. Results: 1) Before treatment, there was no significant difference in baseline values between the two groups (p > 0.05). 2) After 12 months of treatment, the 24-h proteinuria and total cholesterol levels in the RTX/TAC group were significantly lower than those in the P/TAC group (p < 0.05). 3) After 6 months of treatment, the clinical remission rate of the RTX/TAC group was significantly higher than that of the P/TAC group (p < 0.05). After 12 months of treatment, the clinical remission rate of the RTX/TAC group was significantly higher than that of the P/TAC group (p < 0.05). (4) After 3, 6 and 12 months of treatment, serological remission rates in the RTX/TAC group were significantly higher than those in the P/TAC group (p < 0.05). During treatment, the anti-PLA2R antibody titres in the RTX/TAC group remained lower than those in the P/TAC group (p < 0.05). Conclusion: The low-dose RTX combined with low-dose TAC steroid-free regimen induces serological remission in patients with PMN earlier than the classic regimen of P combined with TAC, and there was no significant difference in adverse effects between the two groups. Besides, the long-term clinical remission effect of low-dose RTX combined with low-dose TAC is better than that of P combined with TAC.
Keywords: prednisone; primary membranous nephropathy; rituximab; steroids; tacrolimus.
Copyright © 2024 Xing, Ma, Li, Xu, Ji, Zhu, Luo and Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fernández-Juárez G., Rojas-Rivera J., Logt A. V., Justino J., Sevillano A., Caravaca-Fontán F., et al. (2021). The STARMEN trial indicates that alternating treatment with corticosteroids and cyclophosphamide is superior to sequential treatment with tacrolimus and rituximab in primary membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int. 99 (4), 986–998. 10.1016/j.kint.2020.10.014 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources