Anti-hypertensive effect of a novel angiotensin II receptor neprilysin inhibitor (ARNi) -S086 in DSS rat model
- PMID: 38420263
- PMCID: PMC10899683
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1348897
Anti-hypertensive effect of a novel angiotensin II receptor neprilysin inhibitor (ARNi) -S086 in DSS rat model
Abstract
Introduction: Angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor (ARNi), comprised of an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) and a neprilysin inhibitor (NEPi), has established itself as a safe and effective intervention for hypertension. S086 is a novel ARNi cocrystal developed by Salubris for the treatment of heart failure and hypertension.
Methods: Dahl Salt Sensitive (DSS) hypertensive rat model and telemetry system were employed in this study to investigate the anti-hypertensive efficacy of S086 and compare it with the first ARNi-LCZ696.
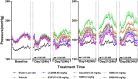
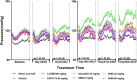
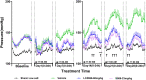
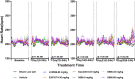
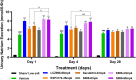
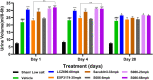
Results and discussion: The study showed that oral administration of S086 dose-dependently lowered blood pressure (P < 0.001). The middle dosage of S086 (23 mg/kg) exhibited efficacy comparable to LCZ696 (68 mg/kg), while also demonstrating superiority at specific time points (P < 0.05). Notably, water consumption slightly decreased post-treatment compared to the vehicle group. Furthermore, there were significant increases in natriuresis and diuresis observed on the first day of treatment with 23 mg/kg and 68 mg/kg S086 (P < 0.001). However, over the course of treatment, the effects in all treatment groups gradually diminished. This study demonstrates the anti-hypertensive efficacy of S086 in DSS hypertensive rat model, offering promising avenues for the clinical development of S086 as a hypertension treatment.
Keywords: angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB); angiotensin receptor-NEP inhibitor (ARNi); diuresis; hypertension; natriuresis; neprilysin inhibitor.
© 2024 Sun, Xiao, Xu, Xing, Du, Tian, Xu, Ren and Fang.
Conflict of interest statement
S086 is Salubris’ developing product, and Salubris is the patent owner. JS, YX, WXu, and WXi were employed by Shenzhen Salubris Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. FD, MT, DD, YR and XF were employed by WuXi AppTec (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic effects of S086, a novel angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Sep;129:110410. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110410. Epub 2020 Jun 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32570118
-
Protective effect of novel angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor S086 on target organ injury in spontaneously hypertensive rats.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Jan;170:115968. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115968. Epub 2023 Dec 1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38039752
-
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, single, and multiple dose-escalation Phase I clinical trial to investigate the safety, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic profiles of oral S086, a novel angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor, in healthy Chinese volunteers.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2022 Sep;31(9):977-985. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2021.1985464. Epub 2021 Nov 8. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2022. PMID: 34633260 Clinical Trial.
-
Potential effects and application prospect of angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor in diabetic kidney disease.J Diabetes Complications. 2022 Jan;36(1):108056. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2021.108056. Epub 2021 Oct 6. J Diabetes Complications. 2022. PMID: 34893426 Review.
-
The Sacubitril/Valsartan, a First-in-Class, Angiotensin Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitor (ARNI): Potential Uses in Hypertension, Heart Failure, and Beyond.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2018 Jan 27;20(1):5. doi: 10.1007/s11886-018-0944-4. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29374807 Review.
Cited by
-
Measurement of blood pressure in rats: Invasive or noninvasive methods?Physiol Rep. 2024 Sep;12(17):e70041. doi: 10.14814/phy2.70041. Physiol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39266877 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revealing Local Structure of Angiotensin Receptor-Neprilysin Inhibitor (S086) Drug Cocrystal by Linear and Nonlinear Infrared Spectroscopies.ACS Omega. 2024 Dec 4;9(50):49683-49691. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c07887. eCollection 2024 Dec 17. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39713634 Free PMC article.
References
-
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: a pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants. Lancet. (2021) 398:957–80. 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01330-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chatelanat O, Pechère-Bertschi A, Ponte B. Sensibilité au sel et hypertension artérielle [Salt sensitivity and hypertension]. Rev Med Suisse. (2019) 15:1625–28. . - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

