Efficient photocatalytic bactericidal performance of green-synthesised TiO2/reduced graphene oxide using banana peel extracts
- PMID: 38420369
- PMCID: PMC10901103
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26636
Efficient photocatalytic bactericidal performance of green-synthesised TiO2/reduced graphene oxide using banana peel extracts
Abstract
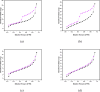
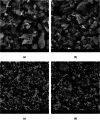
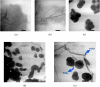
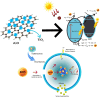
In this study, the fabrication of titanium dioxide/reduced graphene oxide (TiO2/rGO) utilising banana peel extracts (Musa paradisiaca L.) as a reducing agent for the photoinactivation of Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) was explored. The GO synthesis was conducted using a modified Tour method, whereas the production of rGO involved banana peel extracts through a reflux method. The integration of TiO2 into rGO was achieved via a hydrothermal process. The successful synthesis of TiO2/rGO was verified through various analytical techniques, including X-ray diffraction (XRD), gas sorption analysis (GSA), Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, ultraviolet-visible diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (UV-Vis DRS), scanning electron microscope-energy dispersive X-ray (SEM-EDX) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analyses. The results indicated that the hydrothermal-assisted green synthesis effectively produced TiO2/rGO with a particle size of 60.5 nm. Compared with pure TiO2, TiO2/rGO demonstrated a reduced crystallite size (88.505 nm) and an enhanced surface area (22.664 m2/g). Moreover, TiO2/rGO featured a low direct bandgap energy (3.052 eV), leading to elevated electrical conductivity and superior photoconductivity. To evaluate the biological efficacy of TiO2/rGO, photoinactivation experiments targeting E. coli and S. aureus were conducted using the disc method. Sunlight irradiation emerged as the most effective catalyst, achieving optimal inactivation results within 6 and 4 h.
Keywords: E. coli bacteria; Nanocomposite; Photoinactivation; S. aureus bacteria; TiO2/rGO.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Citrus sinensis and Musa acuminata Peel Waste Extract Mediated Synthesis of TiO2/rGO Nanocomposites for Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue under Visible Light Irradiation.Bioinorg Chem Appl. 2022 Jan 25;2022:5978707. doi: 10.1155/2022/5978707. eCollection 2022. Bioinorg Chem Appl. 2022. PMID: 35116062 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic effects and kinetics of rGO-modified TiO2 nanocomposite on adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of humic acid.J Environ Manage. 2019 Apr 1;235:293-302. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.01.026. J Environ Manage. 2019. PMID: 30690325
-
Photocatalytic degradation of naphthol blue from Batik wastewater using functionalized TiO2-based composites.Chemosphere. 2023 Oct;337:139224. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.139224. Epub 2023 Jun 17. Chemosphere. 2023. PMID: 37336442
-
Obtaining titanium dioxide nanoparticles with spherical shape and antimicrobial properties using M. citrifolia leaves extract by hydrothermal method.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2017 Jun;171:117-124. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2017.05.003. Epub 2017 May 3. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2017. PMID: 28501689
-
Effect of surface pretreatment of TiO2 films on interfacial processes leading to bacterial inactivation in the dark and under light irradiation.Interface Focus. 2015 Feb 6;5(1):20140046. doi: 10.1098/rsfs.2014.0046. Interface Focus. 2015. PMID: 25657831 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Harnessing Novel Reduced Graphene Oxide-Based Aerogel for Efficient Organic Contaminant and Heavy Metal Removal in Aqueous Environments.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Oct 26;14(21):1708. doi: 10.3390/nano14211708. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39513788 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguilar S., Guerrero B., Benitez A., Ramos D.R., Santaballa J.A., Canle M., Rosado D., Moreno-Andres J. Inactivation of E. coli and S. Aureus by novel binary clay/seminconductor photocatalytic macrocomposites under UVA and sunlight irradiation. Joirnal of Environmental Chemical Engineering. 2023;1 doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2023.110813. - DOI
-
- Chen Y., Tang X., Gao X., Zhang B., Luo Y., Yao X. Antimicrobial property and photocatalytic antibacterial mechanism of the TiO2-doped SiO2 hybrid materials under ultraviolet-light irradiation and visible-light irradiation. Ceram. Int. 2019;45(12):15505–15513. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.05.054. - DOI
-
- Pérez E., Torres M.F., Morales G., Murgia V., Sham E. Synthesis of N-TiO2 effect of the concentration of nitrogen in the band gap. Procedia Materials Science. 2015;8:649–655. doi: 10.1016/j.mspro.2015.04.121. - DOI
-
- Caratto V., Setti L., Campodonico S., Carnasciali M.M., Botter R., Ferretti M. Synthesis and characterization of nitrogen-doped TiO2 nanoparticles prepared by sol-gel method. J. Sol. Gel Sci. Technol. 2012;63:16–22. doi: 10.1007/s10971-012-2756-0. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

