Regulatory role of T helper 9/interleukin-9: Transplantation view
- PMID: 38420400
- PMCID: PMC10900956
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26359
Regulatory role of T helper 9/interleukin-9: Transplantation view
Abstract
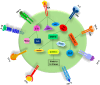
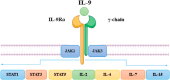
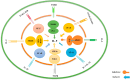
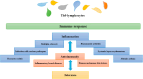
T helper 9 (Th9) cells, a subset of CD4+ T helper cells, have emerged as a valuable target for immune cell therapy due to their potential to induce immunomodulation and tolerance. The Th9 cells mainly produce interleukin (IL)-9 and are known for their defensive effects against helminth infections, allergic and autoimmune responses, and tumor suppression. This paper explores the mechanisms involved in the generation and differentiation of Th9 cells, including the cytokines responsible for their polarization and stabilization, the transcription factors necessary for their differentiation, as well as the role of Th9 cells in inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, allergic reactions, and cancer immunotherapies. Recent research has shown that the differentiation of Th9 cells is coregulated by the transcription factors transforming growth factor β (TGF-β), IL-4, and PU.1, which are also known to secrete IL-10 and IL-21. Multiple cell types, such as T and B cells, mast cells, and airway epithelial cells, are influenced by IL-9 due to its pleiotropic effects.
Keywords: CD4+ T cells; IL-4; IL-9; TGF-β; Th9 cells.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The emerging role of T helper 9 (Th9) cells in immunopathophysiology: A comprehensive review of their effects and responsiveness in various disease states.Int Rev Immunol. 2024;43(6):341-360. doi: 10.1080/08830185.2024.2364586. Epub 2024 Jun 12. Int Rev Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38864109 Review.
-
Th9 and other IL-9-producing cells in allergic asthma.Semin Immunopathol. 2017 Jan;39(1):55-68. doi: 10.1007/s00281-016-0601-1. Epub 2016 Nov 17. Semin Immunopathol. 2017. PMID: 27858144 Review.
-
[The role of Th9 and other IL-9 producing cells in allergic asthma].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018 Nov;32(21):1679-1683. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2018.21.018. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30400697 Review. Chinese.
-
The Differentially Expressed Genes Responsible for the Development of T Helper 9 Cells From T Helper 2 Cells in Various Disease States: Immuno-Interactomics Study.JMIR Bioinform Biotechnol. 2023 Feb 23;4:e42421. doi: 10.2196/42421. JMIR Bioinform Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 38935935 Free PMC article.
-
Th9 Cells: New Member of T Helper Cell Family.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1585:1-19. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6877-0_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28477183
Cited by
-
Immunocytes interact directly with cancer cells in the tumor microenvironment: one coin with two sides and future perspectives.Front Immunol. 2024 May 22;15:1388176. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1388176. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38840908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Th17 cell function in cancers: immunosuppressive agents or anti-tumor allies?Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Oct 27;24(1):355. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03525-9. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 39465401 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

