A brief review and scientometric analysis on ensemble learning methods for handling COVID-19
- PMID: 38420425
- PMCID: PMC10901105
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26694
A brief review and scientometric analysis on ensemble learning methods for handling COVID-19
Abstract
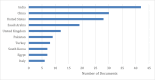
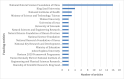
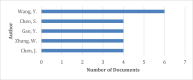
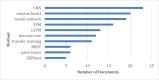
Numerous efforts and research have been conducted worldwide to combat the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. In this regard, some researchers have focused on deep and machine-learning approaches to discover more about this disease. There have been many articles on using ensemble learning methods for COVID-19 detection. Still, there seems to be no scientometric analysis or a brief review of these researches. Hence, a combined method of scientometric analysis and brief review was used to study the published articles that employed an ensemble learning approach to detect COVID-19. This research used both methods to overcome their limitations, leading to enhanced and reliable outcomes. The related articles were retrieved from the Scopus database. Then a two-step procedure was employed. A concise review of the collected articles was conducted. Then they underwent scientometric and bibliometric analyses. The findings revealed that convolutional neural network (CNN) is the mostly employed algorithm, while support vector machine (SVM), random forest, Resnet, DenseNet, and visual geometry group (VGG) were also frequently used. Additionally, China has had a significant presence in the numerous top-ranking categories of this field of research. Both study phases yielded valuable results and rankings.
Keywords: COVID-19; Convolutional neural network; Deep learning; Ensemble learning; Ensemble method.
© 2024 The Author.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Al-Emran M., Al-Kabi M.N., Marques G. A survey of using machine learning algorithms during the COVID-19 pandemic. Emerging technologies during the era of COVID-19 pandemic. 2021:1–8.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

