Ehf and Fezf2 regulate late medullary thymic epithelial cell and thymic tuft cell development
- PMID: 38420512
- PMCID: PMC10901246
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1277365
Ehf and Fezf2 regulate late medullary thymic epithelial cell and thymic tuft cell development
Abstract
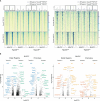
Thymic epithelial cells are indispensable for T cell maturation and selection and the induction of central immune tolerance. The self-peptide repertoire expressed by medullary thymic epithelial cells is in part regulated by the transcriptional regulator Aire (Autoimmune regulator) and the transcription factor Fezf2. Due to the high complexity of mTEC maturation stages (i.e., post-Aire, Krt10+ mTECs, and Dclk1+ Tuft mTECs) and the heterogeneity in their gene expression profiles (i.e., mosaic expression patterns), it has been challenging to identify the additional factors complementing the transcriptional regulation. We aimed to identify the transcriptional regulators involved in the regulation of mTEC development and self-peptide expression in an unbiased and genome-wide manner. We used ATAC footprinting analysis as an indirect approach to identify transcription factors involved in the gene expression regulation in mTECs, which we validated by ChIP sequencing. This study identifies Fezf2 as a regulator of the recently described thymic Tuft cells (i.e., Tuft mTECs). Furthermore, we identify that transcriptional regulators of the ELF, ESE, ERF, and PEA3 subfamily of the ETS transcription factor family and members of the Krüppel-like family of transcription factors play a role in the transcriptional regulation of genes involved in late mTEC development and promiscuous gene expression.
Keywords: Ehf; Fezf2; Tuft cells; central tolerance; medullary thymic epithelial cell; thymus.
Copyright © 2024 Lammers, Barrera, Brennecke, Miller, Yoon, Balolong, Anderson, Ho Sui, Steinmetz, von Andrian and Rattay.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Functionally diverse thymic medullary epithelial cells interplay to direct central tolerance.Cell Rep. 2024 Apr 23;43(4):114072. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114072. Epub 2024 Apr 5. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 38581680 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation profile of Aire-deficient mouse medullary thymic epithelial cells.BMC Immunol. 2012 Nov 2;13:58. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-13-58. BMC Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23116172 Free PMC article.
-
Aire Disruption Influences the Medullary Thymic Epithelial Cell Transcriptome and Interaction With Thymocytes.Front Immunol. 2018 May 7;9:964. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00964. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29867946 Free PMC article.
-
Aire and Fezf2, two regulators in medullary thymic epithelial cells, control autoimmune diseases by regulating TSAs: Partner or complementer?Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 30;13:948259. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.948259. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36110862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Thymus as a Mirror of the Body's Gene Expression.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025;1471:247-268. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-77921-3_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 40067590 Review.
Cited by
-
The Ins and Outs of Thymic Epithelial Cell Differentiation and Function.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025;1471:51-79. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-77921-3_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 40067584 Review.
-
It's Time to Unite: Diversity and Coordination of Thymic Stromal Cells for T Cell Selection and Organ Integrity.Immunol Rev. 2025 Jul;332(1):e70040. doi: 10.1111/imr.70040. Immunol Rev. 2025. PMID: 40464763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generation and repair of thymic epithelial cells.J Exp Med. 2024 Oct 7;221(10):e20230894. doi: 10.1084/jem.20230894. Epub 2024 Jul 9. J Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 38980292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-resolution transcriptional impact of AIRE: effects of pathogenic variants p.Arg257Ter, p.Cys311Tyr, and polygenic risk variant p.Arg471Cys.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 22;16:1572789. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1572789. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40330469 Free PMC article.
-
Antigen presentation for central tolerance induction.Nat Rev Immunol. 2025 Jan;25(1):57-72. doi: 10.1038/s41577-024-01076-8. Epub 2024 Sep 18. Nat Rev Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39294277 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

