Dorsal motor vagal neurons can elicit bradycardia and reduce anxiety-like behavior
- PMID: 38420585
- PMCID: PMC10901094
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109137
Dorsal motor vagal neurons can elicit bradycardia and reduce anxiety-like behavior
Abstract
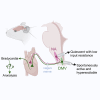
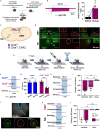
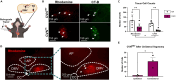
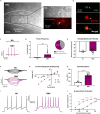
Cardiovagal neurons (CVNs) innervate cardiac ganglia through the vagus nerve to control cardiac function. Although the cardioinhibitory role of CVNs in nucleus ambiguus (CVNNA) is well established, the nature and functionality of CVNs in dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus (CVNDMV) is less clear. We therefore aimed to characterize CVNDMV anatomically, physiologically, and functionally. Optogenetically activating cholinergic DMV neurons resulted in robust bradycardia through peripheral muscarinic (parasympathetic) and nicotinic (ganglionic) acetylcholine receptors, but not beta-1-adrenergic (sympathetic) receptors. Retrograde tracing from the cardiac fat pad labeled CVNNA and CVNDMV through the vagus nerve. Using whole-cell patch-clamp, CVNDMV demonstrated greater hyperexcitability and spontaneous action potential firing ex vivo despite similar resting membrane potentials, compared to CVNNA. Chemogenetically activating DMV also caused significant bradycardia with a correlated reduction in anxiety-like behavior. Thus, DMV contains uniquely hyperexcitable CVNs and is capable of cardioinhibition and robust anxiolysis.
Keywords: Behavioral neuroscience; Biological sciences; Natural sciences; Neuroscience; Physiology; Systems neuroscience.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

Update of
-
Dorsal Motor Vagal Neurons Can Elicit Bradycardia and Reduce Anxiety-Like Behavior.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 17:2023.11.14.566855. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.14.566855. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: iScience. 2024 Feb 06;27(3):109137. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109137. PMID: 38014247 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

