Absence in CX3CR1 receptor signaling promotes post-ischemic stroke cognitive function recovery through suppressed microglial pyroptosis in mice
- PMID: 38421089
- PMCID: PMC10850801
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.14551
Absence in CX3CR1 receptor signaling promotes post-ischemic stroke cognitive function recovery through suppressed microglial pyroptosis in mice
Abstract
Background: Post-stroke cognitive impairment (PSCI) is a major source of morbidity and mortality after stroke, but the pathological mechanisms remain unclear. Previous studies have demonstrated that the CX3CR1 receptor plays a crucial role in maintaining an early protective microenvironment after stroke, but whether it persistently influences cognitive dysfunction in the chronic phase requires further investigation.
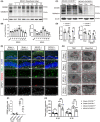
Methods: Mouse was used to establish a middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO)/reperfusion model to study PSCI. Cognitive function was assessed by the Morris water maze (MWM) and the novel object recognition test. Neurogenesis was assessed by immunofluorescence staining with Nestin+ /Ki67+ and DCX+ /BrdU+ double-positive cells. The cerebral damage was monitored by [18 F]-DPA-714 positron emission tomography, Nissel, and TTC staining. The pyroptosis was histologically, biochemically, and electron microscopically examined.
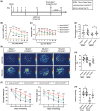
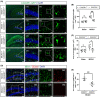
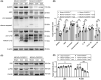
Results: Upon MCAO, at 28 to 35 days, CX3CR1 knockout (CX3CR1-/- ) mice had better cognitive behavioral performance both in MWM and novel object recognition test than their CX3CR1+/- counterparts. Upon MCAO, at 7 days, CX3CR1-/- mice increased the numbers of Nestin+ /Ki67+ and DCX+ /BrdU+ cells, and meanwhile it decreased the protein expression of GSDMD, NLRP3 inflammasome subunit, caspase-1, mature IL-1β/IL-18, and p-P65 in the hippocampus as compared with CX3CR1+/- mice. In addition, CX3CR1-/- mice could reverse infarct volume in the hippocampus region post-stroke.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated that CX3CR1 gene deletion was beneficial to PSCI recovery. The mechanism might lie in inhibited pyroptosis and enhanced neurogenesis. CX3CR1 receptor may serve as a therapeutic target for improving the PSCI.
Keywords: CX3C chemokine receptor 1; cognitive dysfunction; ischemic stroke; microglia.
© 2023 The Authors. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Campbell BCV, De Silva DA, Macleod MR, et al. Ischaemic stroke. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5:70. - PubMed
-
- Ferro JM, Caeiro L, Figueira ML. Neuropsychiatric sequelae of stroke. Nat Rev Neurol. 2016;12:269‐280. - PubMed
-
- Rost NS, Brodtmann A, Pase MP, et al. Post‐stroke cognitive impairment and dementia. Circ Res. 2022;130:1252‐1271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

