Sleep and APOE-ε4 have a synergistic effect on plasma biomarkers and longitudinal cognitive decline in older adults
- PMID: 38421124
- PMCID: PMC10850800
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.14558
Sleep and APOE-ε4 have a synergistic effect on plasma biomarkers and longitudinal cognitive decline in older adults
Abstract
Background: Sleep disorders are prevalent among patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD), and the APOE ε4 genotype is a key genetic risk factor for sporadic AD. However, the combined effect of the genotype and sleep disorders on cognitive decline remains uncertain.
Methods: A total of 972 participants were drawn from the SILCODE cohort, comprising 655 without the ε4 allele (APOE-) and 317 with ε4 allele (APOE+). Data were collected, including neuropsychological assessments, sleep measurements, plasma biomarkers, and PET imaging. A Sleep Composite Index (SCI) was created, categorizing participants into high risk (Sleep+) and low risk (Sleep-).
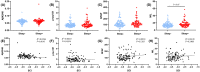
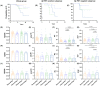
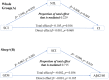
Results: Significant predictions of dementia risk associated with plasma p-tau181, neurofilament light chain (NfL), and SCI. Individuals with both Sleep+ and APOE+ had a higher risk of dementia compared to those with Sleep-. The Sleep+/APOE+ group had higher plasma NfL levels than the Sleep-/APOE- group. Similar trends emerged in plasma NfL levels among the Aβ PET-positive subgroup. Plasma NfL levels explained 23% of the relationship between SCI and cognitive impairment.
Conclusion: Our study highlights sleep disorder was associated with cognitive decline, with plasma NfL playing a partial mediating role. These findings explain how sleep disorders affect cognitive function and emphasize the importance of healthy sleep for older adults.
Keywords: APOE ε4; Alzheimer's disease; biomarkers; discrimination; sleep.
© 2023 The Authors. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Plasma Aβ42/40 ratio, p-tau181, GFAP, and NfL across the Alzheimer's disease continuum: A cross-sectional and longitudinal study in the AIBL cohort.Alzheimers Dement. 2023 Apr;19(4):1117-1134. doi: 10.1002/alz.12724. Epub 2022 Jul 21. Alzheimers Dement. 2023. PMID: 36574591
-
Stage-specific links between plasma neurofilament light and imaging biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease.Brain. 2020 Dec 1;143(12):3793-3804. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa342. Brain. 2020. PMID: 33210117 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma NfL is associated with the APOE ε4 allele, brain imaging measurements of neurodegeneration, and lower recall memory scores in cognitively unimpaired late-middle-aged and older adults.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2023 Apr 10;15(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s13195-023-01221-w. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37038190 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of APOE ε4 and ε2 on plasma neurofilament light chain and cognition in autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024 Oct 1;16(1):208. doi: 10.1186/s13195-024-01572-y. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 39354618 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship Between Sleep Disturbance and Apolipoprotein E ε4 in Adults With Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer's Disease Dementia: An Integrative Review.Biol Res Nurs. 2022 Jul;24(3):327-337. doi: 10.1177/10998004221081044. Epub 2022 Apr 19. Biol Res Nurs. 2022. PMID: 35439097 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein in the Neuropathology of Alzheimer's Disease and Its Potential as a Blood Biomarker for Early Diagnosis and Progression.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jul 21. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-05219-3. Online ahead of print. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40690136 Review.
-
Associations between sleep quality, plasma neurofilament light, and cognition in older adults without dementia.Transl Psychiatry. 2025 May 16;15(1):169. doi: 10.1038/s41398-025-03389-1. Transl Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40379641 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep disorders and Alzheimer's disease: relationship and mechanisms involving neuroinflammation, orexin and Aβ.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2025 Jun 20;22(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s12987-025-00638-9. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2025. PMID: 40542388 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Uddin MS, Tewari D, Mamun AA, et al. Circadian and sleep dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease. Ageing Res Rev. 2020;60:101046. - PubMed
-
- Díaz‐Román M, Pulopulos MM, Baquero M, et al. Obstructive sleep apnea and Alzheimer's disease‐related cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in mild cognitive impairment. Sleep. 2021;44(1):zsaa133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

