[Consensus recommendations on the diagnosis and treatment of hyponatremia from the Austrian Society for Nephrology 2024]
- PMID: 38421476
- PMCID: PMC10904443
- DOI: 10.1007/s00508-024-02325-5
[Consensus recommendations on the diagnosis and treatment of hyponatremia from the Austrian Society for Nephrology 2024]
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Konsensusempfehlungen zur Diagnose und Therapie der Hyponatriämie der Österreichischen Gesellschaft für Nephrologie 2024.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2024 Nov;136(21-22):645. doi: 10.1007/s00508-024-02454-x. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2024. PMID: 39436441 Free PMC article. German. No abstract available.
Abstract
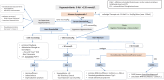
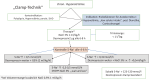
Hyponatremia is a disorder of water homeostasis. Water balance is maintained by the collaboration of renal function and cerebral structures, which regulate thirst mechanisms and secretion of the antidiuretic hormone. Measurement of serum-osmolality, urine osmolality and urine-sodium concentration help to diagnose the different reasons for hyponatremia. Hyponatremia induces cerebral edema and might lead to severe neurological symptoms, which need acute therapy. Also, mild forms of hyponatremia should be treated causally, or at least symptomatically. An inadequate fast increase of the serum sodium level should be avoided, because it raises the risk of cerebral osmotic demyelination. Basic pathophysiological knowledge is necessary to identify the different reasons for hyponatremia which need different therapeutic procedures.
Die Hyponatriämie ist eine Störung des Wasserhaushaltes. Die Wasserhomöostase wird durch das Zusammenspiel von Nierenfunktion und den zerebralen Strukturen des Durstempfindens und der Produktion des antidiuretischen Hormons aufrechterhalten. Durch die Messung der Serum-Osmolalität, Harn-Osmolalität und Harn- Natriumkonzentration können die meisten Ursachen der Hyponatriämie identifiziert werden. Hyponatriämien führen zu einem Hirnödem und können damit schwere neurologische Symptome verursachen, welche eine akute Therapie benötigen. Aber auch milde Formen der Hyponatriämie bedürfen einer, wenn möglich kausalen, oder zumindest symptomatischen Behandlung. Eine inadäquat rasche Korrektur der Hyponatriämie sollte vermieden werden, da diese das Risiko für ein zerebrale osmotische Demyelinisierung erhöht. Da die Art der Therapie eng mit der Ursache der Hyponatriämie zusammenhängt, ist eine Grundkenntnis der pathophysiologischen Prozesse für eine optimale Behandlung notwendig.
Keywords: Cerebral edema; Osmolality; Osmotic demyelination syndrome; Polydipsia; Vasopressin.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Figures



References
-
- Spasovski G, Vanholder R, Allolio B, et al. Clinical practice guideline on diagnosis and treatment of hyponatraemia. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2014;29(2):i1–i39. 10.1093/ndt/gfu040. - PubMed
-
- Lindner G, Schwarz C, Haidinger M, Ravioli S. Hyponatremia in the emergency department. Am J Emerg Med. 2022;60:1–8. 10.1016/j.ajem.2022.07.023. - PubMed
-
- Suárez V, Norello D, Sen E, et al. Impairment of neurocognitive functioning, motor performance, and mood stability in hospitalized patients with euvolemic moderate and profound hyponatremia. Am J Med. 2020;133(8):986–993.e5. 10.1016/j.amjmed.2019.12.056. - PubMed
-
- Renneboog B, Musch W, Vandemergel X, Manto MU, Decaux G. Mild chronic hyponatremia is associated with falls, unsteadiness, and attention deficits. Am J Med. 2006;119(1):71.e1–71.e8. 10.1016/j.amjmed.2005.09.026. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

