Association of NK cell subsets and cytotoxicity with FCGR3A gene polymorphism in functional NK cell deficiency
- PMID: 38422319
- PMCID: PMC10903273
- DOI: 10.1590/1806-9282.20230872
Association of NK cell subsets and cytotoxicity with FCGR3A gene polymorphism in functional NK cell deficiency
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study was to assess the association between clinical, laboratory, and functional analyses and polymorphism in the FCGR3A gene in individuals with functional NK cell deficiency.
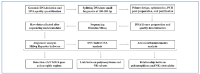
Methods: A total of 15 functional NK cell deficiency patients and 10 age-matched healthy controls underwent NK cell subgroup, cytotoxicity, and FCGR3A whole-exome analysis with next-generation sequencing.
Results: Three different NK cell subsets (CD56brightCD16neg, CD56brightCD16int, and CD56dimCD16hi) were identified. No statistically significant difference was found in the ratio of CD56brightCD16neg cells between patients and controls. CD56brightCD16int and CD56dimCD16hi ratios were found to be significantly lower in patients. As a result of NK cell cytotoxicity analysis, a proportional decrease of K562 amount between patients and controls was found to be statistically significant (p<0.001). In the FCGR3A whole-exome analysis, all patients were found to be homozygous mutant for the c.526G > T (p.V176F) in exon 4, while three patients were homozygous wild type and 12 patients were heterozygous for the c.197T>A (p.L66H) in exon 3.
Conclusion: In this study, a group of pediatric patients with suspected functional NK cell deficiency were evaluated and the findings indicated that NK subsets, cytotoxicity results, and FCGR3A gene polymorphism were found to be correlated with the clinical features. We conclude that this kind of study might contribute to follow-up the patients in time.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rituximab-dependent cytotoxicity by natural killer cells: influence of FCGR3A polymorphism on the concentration-effect relationship.Cancer Res. 2004 Jul 1;64(13):4664-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-2862. Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15231679
-
Genetic and Functional Profiling of CD16-Dependent Natural Killer Activation Identifies Patients at Higher Risk of Cardiac Allograft Vasculopathy.Circulation. 2018 Mar 6;137(10):1049-1059. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.030435. Epub 2017 Nov 2. Circulation. 2018. PMID: 29097449
-
Fc gamma receptor 3A polymorphism and risk for HIV-associated cryptococcal disease.mBio. 2013 Aug 27;4(5):e00573-13. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00573-13. mBio. 2013. PMID: 23982074 Free PMC article.
-
Association between functional FCGR3A F158V and FCGR2A R131H polymorphisms and responsiveness to rituximab in patients with autoimmune diseases: a meta-analysis.Pharmacogenomics J. 2023 Nov;23(6):210-216. doi: 10.1038/s41397-023-00308-9. Epub 2023 May 6. Pharmacogenomics J. 2023. PMID: 37149714 Review.
-
Functional CD32 molecules on human NK cells.Leuk Lymphoma. 1999 Sep;35(1-2):47-56. doi: 10.3109/10428199909145704. Leuk Lymphoma. 1999. PMID: 10512162 Review.
References
-
- Lanier LL, Le AM, Phillips JH, Warner NL, Babcock GF. Subpopulations of human natural killer cells defined by expression of the Leu-7 (HNK-1) and Leu-11 (NK-15) antigens. J Immunol. 1983;131(4):1789–1796. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials