Robust Quantification of Phosphodiesterase-4D in Monkey Brain with PET and 11C-Labeled Radioligands That Avoid Radiometabolite Contamination
- PMID: 38423785
- PMCID: PMC11064827
- DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.123.266750
Robust Quantification of Phosphodiesterase-4D in Monkey Brain with PET and 11C-Labeled Radioligands That Avoid Radiometabolite Contamination
Abstract
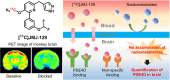
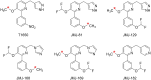
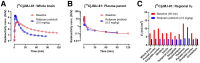
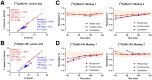
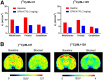
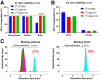
Phosphodiesterase-4D (PDE4D) has emerged as a significant target for treating neuropsychiatric disorders, but no PET radioligand currently exists for robustly quantifying human brain PDE4D to assist biomedical research and drug discovery. A prior candidate PDE4D PET radioligand, namely [11C]T1650, failed in humans because of poor time stability of brain PDE4D-specific signal (indexed by total volume of distribution), likely due to radiometabolites accumulating in brain. Its nitro group was considered to be a source of the brain radiometabolites. Methods: We selected 5 high-affinity and selective PDE4D inhibitors, absent of a nitro group, from our prior structure-activity relationship study for evaluation as PET radioligands. Results: All 5 radioligands were labeled with 11C (half-time, 20.4 min) in useful yields and with high molar activity. All displayed sizable PDE4D-specific signals in rhesus monkey brain. Notably, [11C]JMJ-81 and [11C]JMJ-129 exhibited excellent time stability of signal (total volume of distribution). Furthermore, as an example, [11C]JMJ-81 was found to be free of radiometabolites in ex vivo monkey brain, affirming that this radioligand can provide robust quantification of brain PDE4D with PET. Conclusion: Given their high similarity in structures and metabolic profiles, both [11C]JMJ-81 and [11C]JMJ-129 warrant further evaluation in human subjects. [11C]JMJ-129 shows a higher PDE4D specific-to-nonspecific binding ratio and will be the first to be evaluated.
Keywords: 11C; PET; inhibitors; phosphodiesterase-4D (PDE4D).
© 2024 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Discovery, Radiolabeling, and Evaluation of Subtype-Selective Inhibitors for Positron Emission Tomography Imaging of Brain Phosphodiesterase-4D.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020 May 6;11(9):1311-1323. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00077. Epub 2020 Apr 8. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32212718 Free PMC article.
-
[11C]ZTP-1: An Effective Short-Lived Radioligand for PET of Rat and Monkey Brain Phosphodiesterase Type 4 Subtype B.J Nucl Med. 2025 Jul 1;66(7):1119-1125. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.124.269159. J Nucl Med. 2025. PMID: 40341096
-
An Empirical Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship Equation Assists the Discovery of High-Affinity Phosphodiesterase 4D Inhibitors as Leads to PET Radioligands.J Med Chem. 2023 Jan 26;66(2):1543-1561. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01745. Epub 2023 Jan 6. J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36608175 Free PMC article.
-
PDE4D inhibitors: Opening a new era of PET diagnostics for Alzheimer's disease.Neurochem Int. 2025 Jan;182:105903. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2024.105903. Epub 2024 Dec 6. Neurochem Int. 2025. PMID: 39647702 Review.
-
Considerations in the Development of Reversibly Binding PET Radioligands for Brain Imaging.Curr Med Chem. 2016;23(18):1818-69. doi: 10.2174/0929867323666160418114826. Curr Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27087244 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hooker JM, Carson RE. Human positron emission tomography neuroimaging. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2019;21:551–581. - PubMed
-
- Francis SH, Blount MA, Corbin JD. Mammalian cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: molecular mechanisms and physiological functions. Physiol Rev. 2011;91:651–690. - PubMed
-
- Sun J, Xiao Z, Haider A, et al. . Advances in cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase-targeted PET imaging and drug discovery. J Med Chem. 2021;64:7083–7109. - PubMed
-
- Wachtel H. Potential antidepressant activity of rolipram and other selective cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate phosphodiesterase inhibitors. Neuropharmacology. 1983;22:267–272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
