High-throughput barcoding of nanoparticles identifies cationic, degradable lipid-like materials for mRNA delivery to the lungs in female preclinical models
- PMID: 38424061
- PMCID: PMC10904786
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45422-9
High-throughput barcoding of nanoparticles identifies cationic, degradable lipid-like materials for mRNA delivery to the lungs in female preclinical models
Abstract
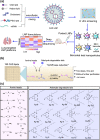
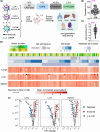
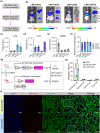
Lipid nanoparticles for delivering mRNA therapeutics hold immense promise for the treatment of a wide range of lung-associated diseases. However, the lack of effective methodologies capable of identifying the pulmonary delivery profile of chemically distinct lipid libraries poses a significant obstacle to the advancement of mRNA therapeutics. Here we report the implementation of a barcoded high-throughput screening system as a means to identify the lung-targeting efficacy of cationic, degradable lipid-like materials. We combinatorially synthesize 180 cationic, degradable lipids which are initially screened in vitro. We then use barcoding technology to quantify how the selected 96 distinct lipid nanoparticles deliver DNA barcodes in vivo. The top-performing nanoparticle formulation delivering Cas9-based genetic editors exhibits therapeutic potential for antiangiogenic cancer therapy within a lung tumor model in female mice. These data demonstrate that employing high-throughput barcoding technology as a screening tool for identifying nanoparticles with lung tropism holds potential for the development of next-generation extrahepatic delivery platforms.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
L.X. and M.J.M. have filed a patent application on this research. D.W. is named on patents that describe the use of nucleoside-modified mRNA as a platform to deliver therapeutic proteins and vaccines. D.W. and M.G.A. are named on patents describing the use of lipid nanoparticles for nucleic acid delivery. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

