Specificity, synergy, and mechanisms of splice-modifying drugs
- PMID: 38424098
- PMCID: PMC10904865
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-46090-5
Specificity, synergy, and mechanisms of splice-modifying drugs
Abstract
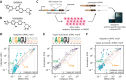
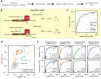
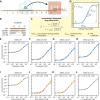
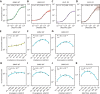
Drugs that target pre-mRNA splicing hold great therapeutic potential, but the quantitative understanding of how these drugs work is limited. Here we introduce mechanistically interpretable quantitative models for the sequence-specific and concentration-dependent behavior of splice-modifying drugs. Using massively parallel splicing assays, RNA-seq experiments, and precision dose-response curves, we obtain quantitative models for two small-molecule drugs, risdiplam and branaplam, developed for treating spinal muscular atrophy. The results quantitatively characterize the specificities of risdiplam and branaplam for 5' splice site sequences, suggest that branaplam recognizes 5' splice sites via two distinct interaction modes, and contradict the prevailing two-site hypothesis for risdiplam activity at SMN2 exon 7. The results also show that anomalous single-drug cooperativity, as well as multi-drug synergy, are widespread among small-molecule drugs and antisense-oligonucleotide drugs that promote exon inclusion. Our quantitative models thus clarify the mechanisms of existing treatments and provide a basis for the rational development of new therapies.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A.R.K. is an inventor on issued nusinersen patents licensed by CSHL to Ionis Pharmaceuticals and Biogen; an inventor on an issued patent for familial dysautonomia ASOs; a co-founder, Director, Chair of the SAB, and shareholder of Stoke Pharmaceuticals; a paid consultant for Biogen; a collaborator of Ionis Pharmaceuticals; and a member of the SABs and shareholder of Skyhawk Pharmaceuticals, Envisagenics, Autoimmunity BioSolutions, and assembl.cns. Other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

