Hippopotamus optimization algorithm: a novel nature-inspired optimization algorithm
- PMID: 38424229
- PMCID: PMC10904400
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-54910-3
Hippopotamus optimization algorithm: a novel nature-inspired optimization algorithm
Abstract
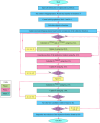
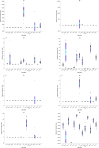
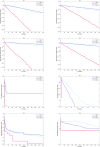
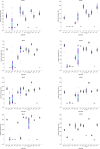
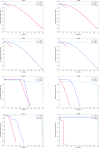
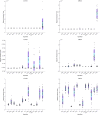
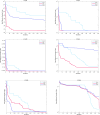
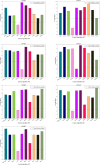
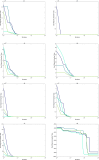
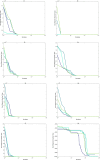
The novelty of this article lies in introducing a novel stochastic technique named the Hippopotamus Optimization (HO) algorithm. The HO is conceived by drawing inspiration from the inherent behaviors observed in hippopotamuses, showcasing an innovative approach in metaheuristic methodology. The HO is conceptually defined using a trinary-phase model that incorporates their position updating in rivers or ponds, defensive strategies against predators, and evasion methods, which are mathematically formulated. It attained the top rank in 115 out of 161 benchmark functions in finding optimal value, encompassing unimodal and high-dimensional multimodal functions, fixed-dimensional multimodal functions, as well as the CEC 2019 test suite and CEC 2014 test suite dimensions of 10, 30, 50, and 100 and Zigzag Pattern benchmark functions, this suggests that the HO demonstrates a noteworthy proficiency in both exploitation and exploration. Moreover, it effectively balances exploration and exploitation, supporting the search process. In light of the results from addressing four distinct engineering design challenges, the HO has effectively achieved the most efficient resolution while concurrently upholding adherence to the designated constraints. The performance evaluation of the HO algorithm encompasses various aspects, including a comparison with WOA, GWO, SSA, PSO, SCA, FA, GOA, TLBO, MFO, and IWO recognized as the most extensively researched metaheuristics, AOA as recently developed algorithms, and CMA-ES as high-performance optimizers acknowledged for their success in the IEEE CEC competition. According to the statistical post hoc analysis, the HO algorithm is determined to be significantly superior to the investigated algorithms. The source codes of the HO algorithm are publicly available at https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/160088-hippopotamus-optimization-algorithm-ho .
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures















References
-
- Dhiman G, Garg M, Nagar A, Kumar V, Dehghani M. A novel algorithm for global optimization: Rat swarm optimizer. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz Comput. 2021;12:8457–8482. doi: 10.1007/s12652-020-02580-0. - DOI
-
- Chen H, et al. An opposition-based sine cosine approach with local search for parameter estimation of photovoltaic models. Energy Convers Manag. 2019;195:927–942. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2019.05.057. - DOI
-
- Li S, Chen H, Wang M, Heidari AA, Mirjalili S. Slime mould algorithm: A new method for stochastic optimization. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020;111:300–323. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2020.03.055. - DOI
-
- Gharaei A, Shekarabi S, Karimi M. Modelling and optimal lot-sizing of the replenishments in constrained, multi-product and bi-objective EPQ models with defective products: Generalised cross decomposition. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2019 doi: 10.1080/23302674.2019.1574364. - DOI
-
- Sayadi R, Awasthi A. An integrated approach based on system dynamics and ANP for evaluating sustainable transportation policies. Int. J. Syst. Sci.: Op. Logist. 2018;7:1–10.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

