Deep Learning Radiomics Analysis of CT Imaging for Differentiating Between Crohn's Disease and Intestinal Tuberculosis
- PMID: 38424279
- PMCID: PMC11300798
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-024-01059-0
Deep Learning Radiomics Analysis of CT Imaging for Differentiating Between Crohn's Disease and Intestinal Tuberculosis
Abstract
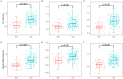
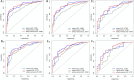
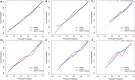
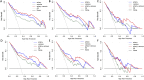
This study aimed to develop and evaluate a CT-based deep learning radiomics model for differentiating between Crohn's disease (CD) and intestinal tuberculosis (ITB). A total of 330 patients with pathologically confirmed as CD or ITB from the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University were divided into the validation dataset one (CD: 167; ITB: 57) and validation dataset two (CD: 78; ITB: 28). Based on the validation dataset one, the synthetic minority oversampling technique (SMOTE) was adopted to create balanced dataset as training data for feature selection and model construction. The handcrafted and deep learning (DL) radiomics features were extracted from the arterial and venous phases images, respectively. The interobserver consistency analysis, Spearman's correlation, univariate analysis, and the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression were used to select features. Based on extracted multi-phase radiomics features, six logistic regression models were finally constructed. The diagnostic performances of different models were compared using ROC analysis and Delong test. The arterial-venous combined deep learning radiomics model for differentiating between CD and ITB showed a high prediction quality with AUCs of 0.885, 0.877, and 0.800 in SMOTE dataset, validation dataset one, and validation dataset two, respectively. Moreover, the deep learning radiomics model outperformed the handcrafted radiomics model in same phase images. In validation dataset one, the Delong test results indicated that there was a significant difference in the AUC of the arterial models (p = 0.037), while not in venous and arterial-venous combined models (p = 0.398 and p = 0.265) as comparing deep learning radiomics models and handcrafted radiomics models. In our study, the arterial-venous combined model based on deep learning radiomics analysis exhibited good performance in differentiating between CD and ITB.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; Deep learning; Diagnosis; Intestinal tuberculosis; Radiomics.
© 2024. The Author(s) under exclusive licence to Society for Imaging Informatics in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A novel multidisciplinary machine learning approach based on clinical, imaging, colonoscopy, and pathology features for distinguishing intestinal tuberculosis from Crohn's disease.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2024 Jul;49(7):2187-2197. doi: 10.1007/s00261-024-04307-7. Epub 2024 May 4. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2024. PMID: 38703189
-
Applying logistic LASSO regression for the diagnosis of atypical Crohn's disease.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 5;12(1):11340. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-15609-5. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35790774 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of increased visceral fat and long segment involvement: Development and validation of an updated imaging marker for differentiating Crohn's disease from intestinal tuberculosis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Jun;33(6):1234-1241. doi: 10.1111/jgh.14065. Epub 2018 Feb 26. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 29205485
-
Differentiating Crohn's disease from intestinal tuberculosis.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Jan 28;25(4):418-432. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i4.418. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30700939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meta-Analytic Bayesian Model For Differentiating Intestinal Tuberculosis from Crohn's Disease.Am J Gastroenterol. 2017 Mar;112(3):415-427. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2016.529. Epub 2017 Jan 3. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28045023 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Applications of artificial intelligence in abdominal imaging.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025 May 26. doi: 10.1007/s00261-025-04990-0. Online ahead of print. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025. PMID: 40418375 Review.
-
Combining radiomics and deep learning to predict liver metastasis of gastric cancer on CT image.Front Oncol. 2025 Jun 24;15:1613972. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1613972. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40630210 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary lipoarabinomannan for gastrointestinal tuberculosis: Another tool in the kit.Indian J Gastroenterol. 2025 Jun 19. doi: 10.1007/s12664-025-01795-3. Online ahead of print. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40536573 No abstract available.
References
-
- Gajendran M, Loganathan P, Catinella AP, Hashash JG: A comprehensive review and update on Crohn's disease. Dis Mon 64:20-57, 2018. - PubMed
-
- Feuerstein JD, Cheifetz AS: Crohn Disease: Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Management. Mayo Clin Proc 92:1088-1103, 2017. - PubMed
-
- Kalra N, Agrawal P, Mittal V, Kochhar R, Gupta V, Nada R, Singh R, Khandelwal N: Spectrum of imaging findings on MDCT enterography in patients with small bowel tuberculosis. Clin Radiol 69:315-322, 2014. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
