Ubiquitylation of RUNX3 by RNA-binding ubiquitin ligase MEX3C promotes tumorigenesis in lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 38424632
- PMCID: PMC10905843
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-023-04700-8
Ubiquitylation of RUNX3 by RNA-binding ubiquitin ligase MEX3C promotes tumorigenesis in lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
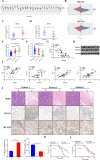
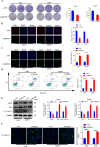
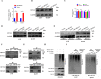
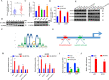
Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is the most common pathological type of lung cancer, but the early diagnosis rate is low. The RNA-binding ubiquitin ligase MEX3C promotes tumorigenesis in several cancers but its mechanism of action in LUAD is unclear. In this study, the biological activity of MEX3C was assessed in LUAD. MEX3C and RUNX3 mRNA levels in the tissues of LUAD patients were determined using reverse transcription‑quantitative PCR. The involvement of MEX3C in the growth and metastasis of LUAD cells was measured by EdU assay, CCK-8, colony formation, Transwell assay, TUNEL, and flow cytometry. Expression of apoptosis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition related proteins were determined using western blotting analysis. LUAD cells transfected with si-MEX3C were administered to mice subcutaneously to monitor tumor progression and metastasis. We found that MEX3C is strongly upregulated in LUAD tissue sections, and involved in proliferation and migration. A549 and H1299 cells had significantly higher levels of MEX3C expression compared to control HBE cells. Knockdown of MEX3C dramatically decreased cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, and accelerated apoptosis. Mechanistically, we demonstrate MEX3C induces ubiquitylation and degradation of tumor suppressor RUNX3. Moreover, RUNX3 transcriptionally represses Suv39H1, as revealed by RNA pull-down and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays. The in vivo mice model demonstrated that knockdown of MEX3C reduced LUAD growth and metastasis significantly. Collectively, we reveal a novel MEX3C-RUNX3-Suv39H1 signaling axis driving LUAD pathogenesis. Targeting MEX3C may represent a promising therapeutic strategy against LUAD.
Keywords: LUAD; MEX3C; Metastasis; RUNX3; Suv39H1; Tumor growth.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
None to declare.
Figures




Similar articles
-
UBE2T promotes stage I lung adenocarcinoma progression through PBX1 ubiquitination and PBX1/RORA regulation.BMC Cancer. 2024 Sep 18;24(1):1158. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12887-2. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39289660 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA circCSNK1G3 induces HOXA10 signaling and promotes the growth and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells through hsa-miR-143-3p sponging.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2021 Apr;44(2):297-310. doi: 10.1007/s13402-020-00565-x. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2021. PMID: 33118120
-
Knockdown of ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2T (UBE2T) suppresses lung adenocarcinoma progression via targeting fibulin-5 (FBLN5).Bioengineered. 2022 May;13(5):11867-11880. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2060162. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35543375 Free PMC article.
-
Junctional adhesion molecule-like protein promotes tumor progression via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in lung adenocarcinoma.J Transl Med. 2022 Jun 7;20(1):260. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03457-w. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35672776 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA GATA6-AS1 upregulates GATA6 to regulate the biological behaviors of lung adenocarcinoma cells.BMC Pulm Med. 2021 May 15;21(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s12890-021-01521-7. BMC Pulm Med. 2021. Retraction in: BMC Pulm Med. 2022 Sep 14;22(1):345. doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-02142-4. PMID: 33992085 Free PMC article. Retracted.
Cited by
-
Identification of the MEX3 family as potential biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma based on bioinformatics and experiments.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 May 30;14(5):2626-2647. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-2095. Epub 2025 May 27. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40530133 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive bioinformatics analysis of MEX3 family genes in hepatocellular carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2025 May 15;15(1):16971. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02057-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40374855 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- No. 2019BYYFYJQ04/the First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars
- No. BY51201314/Bengbu Medical College Science Fund for "Excellent Young Teachers in 512 Talent Development Programme"
- Nos. KJ2021A0692/Natural Science Research Project of Anhui Educational Committee
- KJ2021A0781/Natural Science Research Project of Anhui Educational Committee
- No. BYTM2019013/Translation Medicine Key Project of Bengbu Medical College
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

