Home-based self-management multimodal cancer interventions & cardiotoxicity: a scoping review
- PMID: 38424647
- PMCID: PMC10903028
- DOI: 10.1186/s40959-024-00204-6
Home-based self-management multimodal cancer interventions & cardiotoxicity: a scoping review
Abstract
Background: Due to advancements in methods of cancer treatment, the population of people living with and beyond cancer is dramatically growing. The number of cancer survivors developing cardiovascular diseases and heart failure is also rising, due in part to the cardiotoxic nature of many cancer treatments. Guidelines are being increasingly released, emphasising the need for interdisciplinary action to address this gap in survivorship care. However, the extent to which interventions exist, incorporating the recommendations of cardio-oncology research, remains undetermined.
Objective: The aim of this scoping review is to assess the nature, extent and remit of existing cancer care interventions and their integration of cardio-oncology principles.
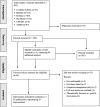
Methods: The review was conducted in accordance with the PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews Guidelines. Databases were independently searched for articles from 2010 to 2022, by two members of the research team. Data were charted and synthesised using the following criteria: (a) the focus of the intervention (b) the medium of delivery (c) the duration (d) the modalities included in the interventions (e) the research articles associated with each intervention (f) the type of studies conducted (g) key measures used (h) outcomes reported.
Results: Interventions encompassed six key modalities: Psychological Support, Physical Activity, Nutrition, Patient Education, Lifestyle and Caregiver Support. The focus, medium of delivery and duration of interventions varied significantly. While a considerable number of study protocols and pilot studies exist documenting HSMIs, only 25% appear to have progressed beyond this stage of development. Of those that have, the present review did not identify any 'feasible' interventions that covered each of the six modalities, while being generalisable to all cancer survivors and incorporating the recommendations from cardio-oncology research.
Conclusion: Despite the substantial volume of research and evidence from the field of cardio-oncology, the findings of this scoping review suggest that the recommendations from guidelines have yet to be successfully translated from theory to practice. There is an opportunity, if not necessity, for cardiac rehabilitation to expand to meet the needs of those living with and beyond cancer.
Keywords: Cancer Interventions; Cardio-Oncology; Cardiotoxicity; Home-Based; Multimodal; Self-Management.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Cancer Research UK. Cancer survival statistics. [cited 2023 Oct 17]. Available from: https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/s...
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer treatment & survivorship facts & figures 2022–2024. 2022. [cited 2023 Oct 17]. Available from: https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-...
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous